Autophagy is required for necrotic cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans (original) (raw)
Main
Several components of the autophagic pathway have been associated with apoptotic cell death.1, 2 For example, inactivation of bec-1 triggers apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans and Bcl-2, an antiapoptotic protein inhibits autophagy by repressing Beclin 1 activity in mammals.3 Autophagy has also been implicated in certain forms of non-apoptotic cell death, in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative conditions caused by expanded polyglutamine-repeat proteins, and in other protein conformation disorders.4, 5, 6, 7, 8 While recent studies also implicate autophagy in necrotic cell death,6, 9, 10, 11 the molecular mechanisms that engage autophagy during necrosis are poorly understood. Specific genetic lesions and environmental conditions trigger necrotic cell death in C. elegans.12 Dying cells exhibit macroscopic and ultrastructural characteristics reminiscent of necrotic cell death caused by excitotoxic insults and hypoxia that follow ischemic incidents in mammals.13 We utilized this well-characterized animal model of necrotic cell death to investigate the involvement of autophagy in necrosis. We systematically examined the requirement for induction of autophagosome formation, in addition to autophagosome nucleation, expansion, completion and retrieval in necrosis. Moreover, we dissected the interaction between autophagy and the lysosomal proteolytic mechanisms that mediate necrotic cell death.
Results
Inhibition of autophagosome formation suppresses necrosis induced by diverse genetic and environmental insults in C. elegans
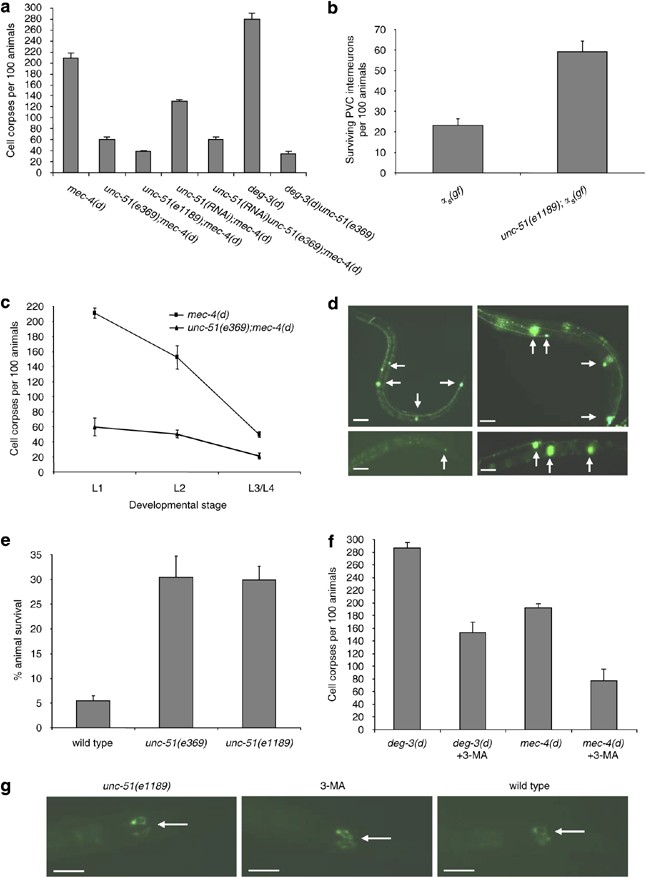
The unc-51 gene encodes the C. elegans ortholog of Atg1, a serine/threonine kinase that is essential for induction of autophagosome formation.14, 15 We find that loss of UNC-51 function strongly suppresses necrotic cell death, initiated by diverse genetically encoded insults in the nematode (Figure 1a and b), consistent with previous observations.10 We examined whether the apparent reduction of necrotic neuron number in animal populations carrying mutations in UNC-51 is the result of delay rather than suppression of cell death. Generally, necrotic cell death triggered by mec-4(d), peaks during the L1 larval stage of C. elegans, with much less cell corpses being observed thereafter.13 We carried out a time-course analysis of necrosis induced by mec-4(d) during all four C. elegans larval stages 1–4 (L1–L4). We did not observe any shift in the cell-death peak to later developmental stages, which would indicate a delay in necrosis (Figure 1c). Moreover, the total number of cell corpses in all stages was significantly reduced by loss of UNC-51 function (131.8±21.6 in unc-51(e369);mec-4(d) double mutants versus 413.1±26.2 in mec-4(d) mutant animals; _n_>1000, P<0.001, unpaired _t_-test). Cell survival was confirmed by scoring for expression of GFP in adult animal neurons (Figure 1d; Supplementary Figure 7).
Figure 1
Induction of autophagy is required for necrotic cell death in C. elegans. (a) Number of neuron corpses, at the L1 larval stage of development, per 100 animals carrying the neurotoxic mec-4(d) or deg-3(d) alleles in genetic backgrounds with UNC-51/Atg1 deficiency (_n_=250; P<0.001, single versus the corresponding double mutant populations, unpaired t_-test). For mec-4(d) mutant animals, bars denote touch receptor neuron corpses. For deg-3(d) mutants, bars denote inner labial neuron 1 (IL1) sensory neuron and PVC interneuron corpses. (b) Surviving PVC interneurons per 100 adult animals with UNC-51/Atg1 deficiency that carry the α_s(gf) allele (_n_=700; P<0.001, unpaired _t_-test). (c) Time-course analysis of _mec-4(d)_-induced necrotic cell death in unc-51(e369);mec-4(d) mutant animals. The number of touch receptor neuron corpses, at the larva stages indicated, per 100 animals is graphed (_n_=300; P<0.001, single versus double mutant populations, unpaired _t_-test). (d) Expression of GFP under the control of the mec-4 promoter in touch receptor neurons of wild type and unc-51 mutant animals (top panels; left and right respectively). Surviving touch receptors, expressing the p_mec-4_GFP transgene, in unc-51(e369);mec-4(d) double mutants (bottom right panel). Fluorescent cells are either absent or barely visible in single mec-4(d) transgenic animals (bottom left panel). Arrows point to touch receptor neurons. White bars denote 50 _μ_m. (e) Percentage of UNC-51/Atg1-deficient animals that survive near-lethal treatment with sodium azide (NaN3; _n_=250; P<0.001, compared to wild-type animals, unpaired _t_-test). Sodium azide inhibits the activity of the respiratory chain electron transport complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase) and simulates hypoxia.16 (f) Number of neuron corpses, at the L1 stage, per 100 animals carrying either the deg-3(d) or the mec-4(d) allele after treatment with 3-methyladenine (3-MA; _n_=250; P<0.001, unpaired _t_-test). Error bars in panels (a–f) denote S.E.M. values. (g) Impairment of autophagy induction in unc-51(e369) mutants (left panel) or after treatment with 3-MA (middle panel), does not affect expression or stability of a full-length MEC-4∷GFP chimera, compared to wild-type animals (right panel). Arrows point to the two PLM touch receptor neurons in the tail. White bars denote 20 _μ_m
Previous genetic studies have implicated UNC-51 in neuron axon elongation and guidance.15 Nervous system wiring defects in unc-51 mutants, result in uncoordinated animal locomotion. We considered whether suppression of neurodegeneration by UNC-51 deficiency is an indirect consequence of abnormal neuron differentiation and the associated phenotypes of unc-51 mutant animals. We used GFP reporter fusions to visualize touch receptor neurons in unc-51 mutants. Despite the distorted morphology of their axons, these neurons express touch receptor-specific reporter genes at typical, wild-type levels (expression of GFP driven by the mec-4 promoter is shown in Figure 1d; see also Figure 3 for the touch receptor-specific gene mec-7 and Supplementary Figure 4 for quantification of full-length, GFP-tagged MEC-4). Consequently, unc-51 mutant animals display normal response to light touch stimuli during adulthood, indicating that touch receptor neurons are functional. Moreover, the double mutants we examined for neurodegeneration do not show any discernible growth defects that could influence the course of necrotic cell death, which peaks during the L1 larva stage.
In addition to genetic mutations, prolonged hypoxia, a condition of low oxygen availability that transpires in ischemic episodes and stroke, also induces necrotic cell death in the nematode.16 UNC-51 deficiency protected animals from hypoxia-induced death (Figure 1e). Our observations reveal a broad requirement for a functional UNC-51 kinase in necrosis and suggest that induction of autophagy is involved in cellular destruction during neurodegeneration in C. elegans.
To establish further the role of autophagosome formation in necrotic cell death, we treated animals carrying the deleterious mec-4(d) or deg-3(d) alleles with 3-methyladenine (3-MA), a compound that perturbs formation of autophagosomes by compromising the activity of class-III phosphatidylinositol-3 (PI3) kinases.17 3-MA ameliorated neuron necrosis in these animals (Figure 1f). We considered whether suppression of _mec-4(d)_-induced cell death by loss of UNC-51 function or by 3-MA treatment is a consequence of a mere reduction in the toxic MEC-4(d) protein levels. We assayed the relative expression, stability and subcellular localization of MEC-4 by utilizing a full-length MEC-4∷GFP reporter fusion. Fusion protein levels and subcellular localization were not affected by genetic or pharmacological manipulations that reduce autophagosome formation (Figure 1g; quantification of fluorescence intensity is shown in Supplementary Figure 4a). We conclude that impairment of autophagosome formation suppresses necrosis in C. elegans.
Autophagosome nucleation, expansion/completion and retrieval is required for necrotic cell death
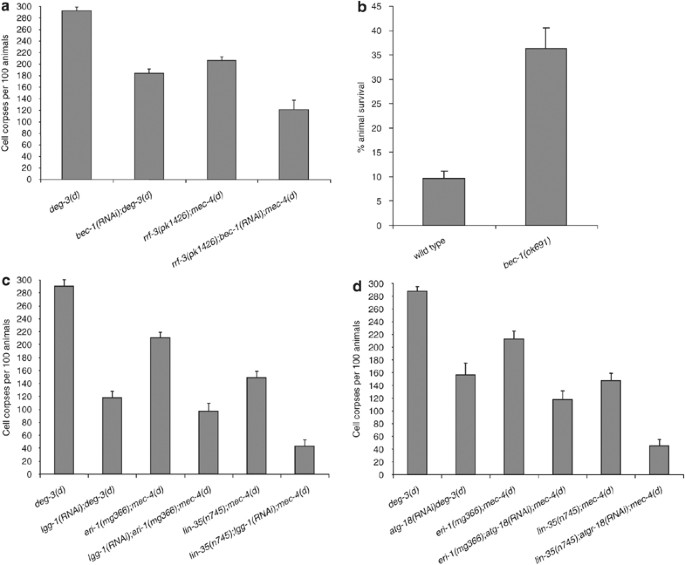
Autophagy is a dynamic, catabolic process that involves multiple, tightly regulated steps. Each of these steps is orchestrated by the concerted action of several atg genes.18 In addition to unc-51, more than a dozen homologs of autophagy genes are encoded in the C. elegans genome14 (CS and NT unpublished observations). We investigated whether necrosis requires the activity of additional genes that mediate discrete autophagic steps, including autophagosome nucleation, autophagosome expansion and completion, and retrieval of Atg protein complexes from mature autophagosomes. We assayed neurodegeneration induced by toxic deg-3(d) and mec-4(d) alleles in animals, where key regulators of these steps were compromised by RNAi. bec-1 encodes the C. elegans ortholog of the yeast autophagy gene Atg6/Vps30 and shows 31% similarity with human Beclin 1.14 Atg6 mediates autophagic vesicle nucleation by forming a complex with the Vps34 class III PI3 kinase.19, 20 We find that neurodegeneration is ameliorated by RNAi with bec-1 (Figure 2a). In addition, bec-1 deletion mutants are significantly more resistant to hypoxia-induced death, compared to wild type (Figure 2b). Next, we examined the requirement for autophagosome expansion and completion in necrotic cell death. In C. elegans, lgg-1 encodes the ortholog of Atg8/LC3, a ubiquitin-like, microtubule-associated protein that facilitates autophagic vesicle growth.21, 22 During autophagosome expansion, Atg8 becomes conjugated with phosphatidylethanolamine at its C terminus and remains attached to autophagosomes after their formation is completed.22 Knockdown of lgg-1 by RNAi suppresses neurodegeneration in C. elegans (Figure 2c). Finally, we investigated the role of the retrieval pathway, essential for disassembly of Atg protein complexes from mature autophagosomes, in necrosis. Atg18, a peripheral membrane protein that binds phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate is required for Atg complex retrieval.23 We observed that RNAi knockdown of the orthologous atgr-18 gene protects from necrotic cell death in C. elegans (Figure 2d).
Figure 2
Autophagosome formation and maturation is required for necrotic cell death in C. elegans. (a) Knockdown of bec-1, involved in autophagic vesicle nucleation ameliorates necrosis. (b) Knockdown of bec-1 significantly increases survival under hypoxic conditions. The percentage of animals that survive near-lethal treatment with sodium azide is shown (_n_=250; P<0.001, compared to wild-type animals, unpaired _t_-test). (**c**) Knockdown of _lgg-1_, which is essential for autophagosome expansion and completion suppresses necrotic cell death. (**d**) Knockdown of _atgr-18_, implicated in of Atg protein complex disassembly and retrieval from mature autophagosomes inhibits necrosis. The number of neuron corpses, at the L1 stage, per 100 animals carrying either the neurotoxic _deg-3(d)_ or _mec-4(d)_ alleles is shown. Error bars denote S.E.M. values (_n_>250 in all experiments; P<0.001, compared to the corresponding control populations, unpaired _t_-test). The RNAi-hypersensitive rrf-3(pk1426), eri-1(mg366) and lin-35(n745) genetic backgrounds were used to enhance bec-1(RNAi), lgg-1(RNAi) and atgr-18(RNAi) effects on _mec-4(d)_-induced neurodegeneration, as indicated. Efficacy of RNAi was assessed as described in the Materials and Methods section (see also Supplementary Information)
Autophagosome formation is induced during necrosis
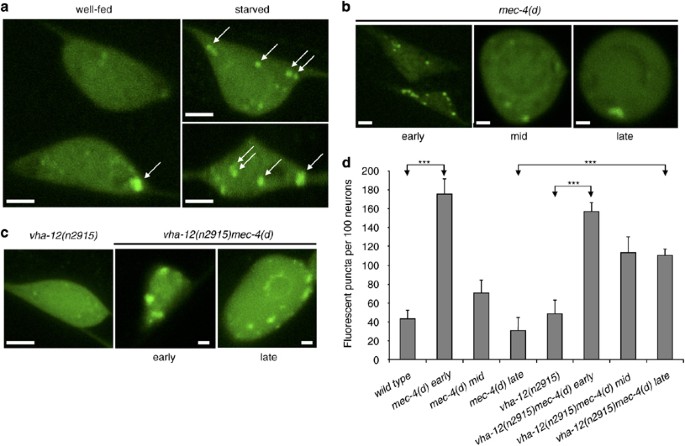
Our genetic analysis demonstrates a requirement for genes that regulate autophagy induction, autophagosome formation and Atg protein retrieval in necrotic cell death (analysis of additional autophagy genes is shown in Supplementary Figure 6). To establish further the role of autophagy in necrosis, we monitored autophagosome formation during neurodegeneration, in vivo. To visualize autophagosomes, we fused both GFP and DsRED to the N terminus of LGG-1/Atg8, which is incorporated in autophagic vesicles during autophagy.21, 22 The fluorescent reporter fusion was expressed specifically in the six touch receptor neurons of wild type and mec-4(d) mutant animals. In well-fed, wild-type animals, neurons appeared diffusely fluorescent, whereas intensely labelled cytoplasmic puncta formed in neurons of animals grown under starvation, a condition known to induce autophagy (Figure 3a).24 This observation indicates that the GFP∷LGG-1 fusion protein is localized to autophagosomes during autophagy in C. elegans neurons. We observed a similar punctate distribution of GFP∷LGG-1 early during degeneration of touch receptors in mec-4(d) mutants (3 h around egg hatching; Figure 3b and d; Supplementary Figures 1 and 2). The number of fluorescent puncta declined through the course of cell death (2–4 h after hatching), while they frequently coalesced into a single aggregate (4–6 h after hatching; Figure 3b and d; Supplementary Figure 1). The large increase in autophagosome number indicates extensive induction of autophagy during early neurodegeneration. The drop in autophagosome abundance at later stages of necrosis may reflect their withdrawal and disintegration by the lysosomal degradation system.25 Lysosomal acidification by the vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multi-subunit proton pump, is important for fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes under conditions of autophagy upregulation.26 We find that under non-inducing conditions the number of autophagosomes in touch receptor neurons is unaffected by a lesion in the vha-12 gene, which encodes the essential B subunit of the peripheral V-ATPase domain V1 (Figure 3c and d). By contrast, autophagosomes persist in dying neurons of mec-4(d) mutant animals with VHA-12 deficiency (Figure 3c and d). Therefore, impaired docking and fusion with lysosomes evokes accumulation of autophagosomes in degenerating neurons of animals with defective V-ATPase. Taken together, our findings suggest that excessive autophagosome formation is induced early during necrotic cell death, in C. elegans.
Figure 3
Excessive autophagosome formation is induced early during necrotic cell death in nematode neurons. (a–c) Confocal images of touch receptor neurons expressing a p_mec-7_GFP∷LGG-1 reporter transgene. White bars denote 2 _μ_m. (a) Neurons of well-fed (left panel) and starved (right panels) wild-type animals. Under starvation conditions, which are known to induce autophagy, GFP∷LGG-1 accumulates in numerous distinct cytoplasmic puncta (some are indicated by arrows). (b) Distribution of GFP∷LGG-1 during the course of degeneration in _mec-4(d)_-expressing neurons. The number of fluorescent dots increases at early stage (1 h prior egg hatching to 2 h after hatching into the L1 larval stage); while it declines as degeneration proceeds and neurons become distended (mid-stage: 2–4 h after hatching; late stage: 4–6 h after hatching). (c) Neuronal distribution pattern of GFP∷LGG-1 in animals with impaired V-ATPase function (left panel) and animals that also carry the neurotoxic mec-4(d) allele (middle and right panels). Fluorescent, GFP∷LGG-1 puncta persist in degenerating neurons of animals carrying a lesion in the vha-12 gene, which encodes the V-ATPase B subunit. (d) Quantification of fluorescent puncta per touch receptor neuron in wild-type animals and the genetic backgrounds indicated. Error bars denote S.E.M. values (_n_=250 in all experiments; ***P<0.001, unpaired _t_-test)
Autophagy synergizes with lysosomal proteolytic pathways to facilitate necrosis
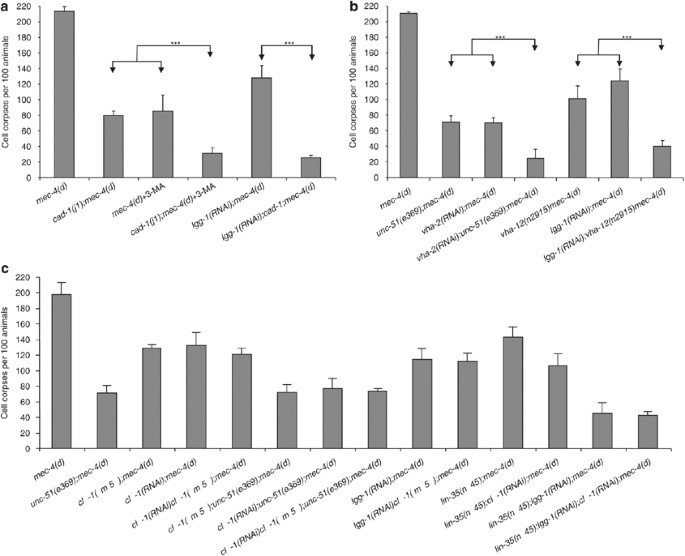
Autophagosomes are ultimately delivered to lysosomes, where their cargo is degraded.18, 24 We examined the interaction of autophagy with these proteolytic mechanisms that contribute to cellular destruction during necrotic cell death. _mec-4(d)_-induced neurodegeneration is ameliorated in lysosomal aspartyl protease-deficient cad-1(j1) mutant animals (Figure 4a; see also Supplementary Figure 8). Suppression of necrosis in cad-1(j1);mec-4(d) double mutants is significantly enhanced by treatment with 3-MA (Figure 4a). Similarly, knockdown of lgg-1 further improved cell survival in cad-1(j1);mec-4(d) animals (Figure 4a). In addition to aspartyl protease activity, V-ATPase-mediated acidification of lysosomes is required for neurodegeneration.27 Low pH is optimal for the function of catabolic lysosomal proteases. To diminish V-ATPase activity, we targeted genes encoding key subunits of both the membrane-integral V0 domain and the peripheral V1 domain of the pump. Knockdown of vha-2, which encodes the essential c subunit of membrane-integral, V0 domain of V-ATPase augmented suppression of necrosis in UNC-51-deficient mutants (Figure 4b). Likewise, knockdown of lgg-1 increased neuron survival in animals with compromised VHA-12 function, where lysosomal acidification is impaired (Figure 4b). Our observations show that autophagy and lysosomal proteolytic mechanisms synergize to facilitate necrotic cell death.
Figure 4
Autophagy synergizes with lysosomal proteolytic mechanisms to facilitate necrotic cell death in C. elegans. (a) Suppression of _mec-4(d)_-induced necrosis by aspartyl protease deficiency in cad-1(j1) mutant animals is enhanced by conditions that impede the autophagic process (3-MA treatment, lgg-1(RNAi)). (b) Autophagy and V-ATPase function are both required for necrotic cell death. Knockdown of vha-2 and vha-12, further protects neurons of animals with defective autophagy induction or autophagosome formation (unc-51(e369) and lgg-1(RNAi), respectively), from _mec-4(d)_-induced necrosis. (c) Knock down of the calpain gene clp-1 does not further suppress _mec-4(d)_-induced necrosis in animals with impaired autophagy. The number of touch receptor neuron corpses, per 100 L1-stage animals is shown. Error bars denote S.E.M. values (_n_>300 in all experiments; ***P<0.001, unpaired _t_-test). Efficacy of RNAi was assessed as described in the Materials and Methods section (see also Supplementary Information)
In addition to the lysosomal system, calpain protease activity is also required for necrosis in C. elegans.28 We investigated the potential link between calpain activity and autophagy in neurodegeneration. Calpain CLP-1 depletion ameliorates necrotic cell death induced by mec-4(d) (Figure 4c). We used both RNAi and a genetic lesion to knockdown clp-1 in mec-4(d) animals with impaired autophagy. We find that knock down of clp-1 does not further suppress necrosis (Figure 4c). Thus, CLP-1 and autophagy function in the same pathway to mediate cell death. Our results are consistent with recent studies implicating calpains in autophagy induction.29, 30 It is likely that calpains exert multiple effects to influence cell death, one of which is via regulation of autophagy. Indeed, calpain activity has been implicated in mediating lysosomal rupture during necrosis both in C. elegans and in mammals.27, 31, 32
Discussion
While the link between autophagy and apoptosis has been studied in depth, the role of autophagy in necrosis has remained unclear. In this study, we utilized an exceptionally well-characterized and genetically tractable model of necrotic cell death in C. elegans to dissect the involvement of autophagy in necrosis. Our findings reveal that autophagy is required for the necrotic breakdown of nematode neurons. Moreover, we provide evidence that excessive autophagy is induced upon commencing of necrotic cell death, and show that autophagy and lysosomal proteolysis combine to promote cell demise. Interestingly, the levels of key autophagy regulators such as Atg6/Beclin 1 and Atg8/LC3 are substantially elevated after traumatic brain injury.33, 34 In addition, excessive autophagy accompanies acute excitotoxic death of hippocampal pyramidal neurons, induced by the _N_-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor (GLR) agonist NMDA and is also induced in dying Purkinje cells of lurcher mice expressing an activated form of the delta 2 GLR.35, 36 We propose that runaway autophagy is an important, conserved mechanism of cellular destruction during necrotic cell death. Preventing aberrant induction of autophagy may reduce cell damage during acute neurodegenerative episodes such as ischemic stroke.
Materials and Methods
Strains and genetics
We followed standard procedures for C. elegans strain maintenance, crosses and other genetic manipulations.37 Nematode rearing temperature was kept at 20°C unless noted otherwise. The following strains were used in this study: N2 (wild-type strain-Bristol isolate), VC517: bec-1(ok691)IV/nT1[qIs51](IV;V), clp-1(tm858)III, TU1747: deg-3(u662)V, referred to in the text as deg-3(d), GR1373: eri-1(mg366)IV, MT10430: lin-35(n745)I, mec-4(u231)X, referred to in the text as mec-4(d), NL2099: rrf-3(pk1426)II, CB369: unc-51(e369)I, CB1189: unc-51(e1189)I, MT7907: vha-12(n2915)X and KP137: _nuIs5_[p_glr-1_G_α_s(Q227L)p_glr-1_GFP], referred to in the text as α s (gf). The following double and multiple mutant strains were examined for neurodegeneration in the study: cad-1(j1);mec-4(u231)X, eri-1(mg366)IV;mec-4(u231)X, lin-35(n745)I;mec-4(u231)X, rrf-3(pk1426)II;mec-4(u231)X, unc-51(e369)I;clp-1(tm858)III;mec-4(d)X, clp-1(tm858)III;mec-4(d)X, vha-12(n2915)mec-4(u231)X, unc-51(e369)I;mec-4(u231)X, unc-51(e1189)I;mec-4(u231)X, unc-51(e369)I;deg-3(u662)V, _unc-51(e1189)I;nuIs5_[p_glr-1_G_α_s(Q227L)p_glr-1_GFP], unc-51(e1189)I;mec-4(u231)X. To verify that mutations in unc-51 do not interfere with touch receptor neuron formation or expression of the toxic mec-4 allele, we examined the following strains, carrying extrachromosomal arrays: _N2;Ex_[p_mec-4_GFP], mec-4(u231)X;_Ex_[p_mec-4_GFP], _unc-51(e369);Ex_[p_mec-4_GFP], _N2;Ex_[p_mec-4_MEC-4∷GFP], _unc-51(e1189); Ex_[p_mec-4_MEC-4∷GFP], _unc-51(e369);mec-4(u231);Ex_[p_mec-4_GFP], _N2;Ex_[p_mec-7_GFP∷LGG-1], _mec-4(u231);Ex_[p_mec-7_GFP∷LGG-1], _vha-12(n2915);Ex_[p_mec-7_GFP∷LGG-1] and _vha-12(n2915)mec-4(u231);Ex_[p_mec-7_GFP∷LGG-1], _N2;Ex_[p_mec-17_BEC-1∷GFP], _mec-4(u231);Ex_[p_mec-17_BEC-1∷GFP], _N2;Ex_[p_lgg-1_dsRed∷LGG-1], zdIs5_[p_mec-4_GFP]I;Ex_[p_lgg-1_dsRed∷LGG-1], zdIs5_[p_mec-4_GFP]I; mec-4(u231)X;Ex_[p_lgg-1_dsRed∷LGG-1], _N2;Ex_[p_lgg-1_dsRed∷LGG-1; p_mec-17_LMP-1∷GFP], _mec-4(u231)X;Ex_[p_lgg-1_dsRed∷LGG-1; p_mec-17_LMP-1∷GFP], N2;_Ex_[p_lgg-1_DsRED∷LGG-1;p_mec-7_mitoGFP] and _mec-4(u231)X;Ex_[p_lgg-1_DsRED∷LGG-1;p_mec-7_mitoGFP].
Plasmid constructs and RNA interference
To generate the lgg-1 reporter construct, we fused GFP at the N terminus of C. elegans LGG-1. The C-terminal amino-acid sequence is cleaved during processing of the mammalian homolog MAP-1 LC3.21 The fusion is placed under the control of the mec-7 promoter, which drives expression in touch receptor neurons. The reporter construct was injected into the gonads of N2 animals together with pRF4, a plasmid that carries the rol-6(su1006), dominant transformation marker. Transgenic roller hermaphrodites were crossed with mec-4(d) males, while transgenic roller males were crossed with mec-4(d) and vha-12(n2915)mec-4(d) hermaphrodites to obtain mutants carrying the autophagosomal marker. To generate the p_lgg-1_DsRED∷LGG-1 reporter construct, we fused DsRED at the N terminus of C. elegans LGG-1. A 750-bp fragment containing the lgg-1 gene was amplified and inserted at the C terminus of DsRED. The reporter fusion was placed under the lgg-1 promoter. To obtain the promoter, we amplified a 1934-bp fragment upstream of the lgg-1 gene. The reporter construct was injected into the gonads of N2 animals together with a plasmid that carries a p_myo-2_GFP reporter fusion, expressing GFP in the pharyngeal muscle cells, as a transformation marker. For p_mec-7_mitoGFP, an _Eco_RI–_Bam_HI fragment containing the GFP coding sequence with an N-terminal mitochondrial localization signal was isolated from plasmid pPD96.32 and inserted downstream of the mec-7 promoter between the _Eco_RI–_Bgl_II restriction sites of the pPD96.41 plasmid vector.38 For p_mec-17_BEC-1∷GFP, a _Bam_HI fragment (∼3 kb) containing the bec-1 coding region was amplified from C. elegans genomic DNA and cloned into the _Bam_HI site of plasmid p_mec-17_GFP (see Supplementary Materials and Methods for more information). Construction of p_mec-17_GFP and p_mec-17_LMP-1∷GFP has been described previously.31 For RNAi experiments, we constructed plasmids that direct the synthesis of dsRNAs corresponding to the genes of interest (see below), in Escherichia coli bacteria, which were then fed to animals, according to a previously described methodology.39 To augment RNAi, animals were reared for two generations on dsRNA-producing E. coli bacteria before examination. To construct the RNAi plasmids, gene-specific fragments were obtained by PCR amplification directly from C. elegans genomic DNA using appropriate primer sets (see Supplementary Materials and Methods). The PCR-generated fragments were subcloned into the pL4440 plasmid vector and resulting constructs were transformed into HT115(DE3) E. coli bacteria, deficient for RNase-E.39
Cell death assays
Degeneration of specific sets of neurons in animals bearing deg-3(d), mec-4(d) alleles was quantified as described previously.27 We quantified α s _(gf)_-induced necrosis by counting surviving PVC interneurons in the tail of animals carrying the _nuIs5_[p_glr-1_G_α_s(Q227L)p_glr-1_GFP] integrated array.40 To infer statistical significance, we typically analyze developmentally synchronized animal cohorts of at least 100 individuals in each of three independent experiments for necrotic cell corpses. To induce hypoxic conditions, nematodes at the L4 stage of development were selected, washed 2–3 times with 1 ml M9 and incubated for 40 min at 20°C with 0.5 M freshly made NaN3 (Sigma, Munich Germany) in M9.16 Worms were washed with M9 and placed into NGM plates to recover. The percentage of living worms was calculated after 12–16 h of recovery. For 3-methyladenine (3-MA) treatment, young adult mec-4(d) cad-1(j1);mec-4(d) and deg-3(d) animals were incubated with 10 mM 3-MA (Sigma) in liquid cultures supplemented with E. coli bacteria for 15–20 h at 20°C. Neurodegeneration was assayed in the progeny of treated animals at the L1 stage of development. For time-course analysis of necrotic cell death, synchronized animal populations were obtained by collecting embryos from gravid adults within a narrow time window of 4 h. For each genetic background examined these populations were divided by three, with each subpopulation including at least 100 individuals. Neuron corpses were counted in each subpopulation at a different developmental stage (indicated in Figure 1c). The total number of corpses was calculated as the sum of the three counts for each subpopulation.
Microscopy and quantification of autophagosome formation
Animals were mounted in 2% agarose pads, anesthetized with 10 mM sodium azide and observed at room temperature. Worms carrying the LGG-1 reporter construct were harvested at the L1–L2 developmental stages and observed using a high magnification oil-objective lens (× 63, Zeiss Plan-NEOFLUAR; numerical aperture1.4; Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany), on a confocal microscope (Zeiss Axioscop with a Bio-Rad Radiance 2100 scanhead, Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA), using the Bio-Rad LaserSharp 2000 software package. To acquire images from individual neurons, animals were scanned with a 488 nm laser beam. Emitted light was gathered using a 515±15 nm band-pass filter. The number of GFP∷LGG-1 dots in each PLM and ALM neuron was counted. In mec-4(d) mutants, neurons were divided into three categories: distended, misshaped and morphologically undistorted, and dots were scored separately in each group. The mean number of dots per neuron was then calculated. For quantification of GFP emission, transgenic animals were photographed using a 480±10 nm band-pass excitation filter on an epifluorescence microscope. Images were acquired using a 515±15 nm band-pass emission filter. Emission intensity was measured on grayscale images with a pixel depth of eight bit (256 shades of gray). We calculated the mean and maximum pixel intensity for each cell in these images using the ImageJ software (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/). For each transgenic line, we processed at least 100 cells images in three independent trials.
Abbreviations
ATG:
autophagy gene
ATGR:
autophagy-related
BEC:
Beclin
CAD:
Cathepsin D
CLP:
Calpain
DEG:
degenerin
DsRed:
Discosoma genus red fluorescent protein
ERI:
enhanced RNAi
G_α_:
G protein _α_-subunit
GABARAP:
GABA(A) receptor-associated protein
GATE-16:
Golgi-associated ATPase enhancer of 16 kDa
gf:
gain of function
GFP:
green fluorescent protein
GLR:
glutamate receptor
IL1:
inner labial neuron 1
L1–L4:
larval stages 1–4
LGG:
LC3, GABARAP and GATE-16
LIN:
lineage
LMP:
lysosomal membrane protein
3-MA:
3-methyladenine
MAP-LC3:
microtubule-associated protein light chain 3
MEC:
mechanosensory
mitoGFP:
mitochondrial GFP
N2:
wild-type C. elegans strain-Bristol isolate
NMDA:
_N_-methyl-D-aspartate
PI3:
phosphatidylinositol-3
PLM:
posterior lateral microtubule neuron
PVC:
posterior ventral cord interneuron
RNAi:
RNA interference
RRF:
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase family
UNC:
uncoordinated
VHA:
Vacuolar H+ ATPase
VPS:
vacuolar protein sorting
V-ATPase:
vacuolar H+-ATPase
WT:
wild type
References
- Baehrecke EH . Autophagy: dual roles in life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 505–510.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Levine B . Eating oneself and uninvited guests: autophagy-related pathways in cellular defense. Cell 2005; 120: 159–162.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005; 122: 927–939.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Cuervo AM . Autophagy: in sickness and in health. Trends Cell Biol 2004; 14: 70–77.
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 2005; 1: 112–119.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E, Welsh S et al. Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 2004; 304: 1500–1502.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Ravikumar B, Vacher C, Berger Z, Davies JE, Luo S, Oroz LG et al. Inhibition of mTOR induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 585–595.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Shibata M, Lu T, Furuya T, Degterev A, Mizushima N, Yoshimori T et al. Regulation of intracellular accumulation of mutant Huntingtin by Beclin 1. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 14474–14485.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Erlich S, Shohami E, Pinkas-Kramarski R . Neurodegeneration induces upregulation of Beclin 1. Autophagy 2006; 2: 49–51.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Toth ML, Simon P, Kovacs AL, Vellai T . Influence of autophagy genes on ion-channel-dependent neuronal degeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Sci 2007; 120: 1134–1141.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Yue Z . Regulation of neuronal autophagy in axon: implication of autophagy in axonal function and dysfunction/degeneration. Autophagy 2007; 3: 139–141.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Syntichaki P, Tavernarakis N . The biochemistry of neuronal necrosis: rogue biology? Nat Rev Neurosci 2003; 4: 672–684.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Hall DH, Gu G, Garcia-Anoveros J, Gong L, Chalfie M, Driscoll M . Neuropathology of degenerative cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 1997; 17: 1033–1045.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Melendez A, Talloczy Z, Seaman M, Eskelinen EL, Hall DH, Levine B . Autophagy genes are essential for dauer development and life-span extension in C. elegans. Science 2003; 301: 1387–1391.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Ogura K, Wicky C, Magnenat L, Tobler H, Mori I, Muller F et al. Caenorhabditis elegans unc-51 gene required for axonal elongation encodes a novel serine/threonine kinase. Genes Dev 1994; 8: 2389–2400.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Scott BA, Avidan MS, Crowder CM . Regulation of hypoxic death in C. elegans by the insulin/IGF receptor homolog DAF-2. Science 2002; 296: 2388–2391.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Seglen PO, Gordon PB . 3-Methyladenine: specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1982; 79: 1889–1892.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Klionsky DJ . The molecular machinery of autophagy: unanswered questions. J Cell Sci 2005; 118: 7–18.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Kametaka S, Okano T, Ohsumi M, Ohsumi Y . Apg14p and Apg6/Vps30p form a protein complex essential for autophagy in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 22284–22291.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Kihara A, Noda T, Ishihara N, Ohsumi Y . Two distinct Vps34 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complexes function in autophagy and carboxypeptidase Y sorting in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol 2001; 152: 519–530.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T et al. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J 2000; 19: 5720–5728.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Kirisako T, Baba M, Ishihara N, Miyazawa K, Ohsumi M, Yoshimori T et al. Formation process of autophagosome is traced with Apg8/Aut7p in yeast. J Cell Biol 1999; 147: 435–446.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Reggiori F, Tucker KA, Stromhaug PE, Klionsky DJ . The Atg1-Atg13 complex regulates Atg9 and Atg23 retrieval transport from the pre-autophagosomal structure. Dev Cell 2004; 6: 79–90.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Levine B, Klionsky DJ . Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 2004; 6: 463–477.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Kroemer G, Jaattela M . Lysosomes and autophagy in cell death control. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 886–897.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Yamamoto A, Tagawa Y, Yoshimori T, Moriyama Y, Masaki R, Tashiro Y . Bafilomycin A1 prevents maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line, H-4-II-E cells. Cell Struct Funct 1998; 23: 33–42.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Syntichaki P, Samara C, Tavernarakis N . The vacuolar H(+)-ATPase mediates intracellular acidification required for neurodegeneration in C. elegans. Curr Biol 2005; 15: 1249–1254.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Syntichaki P, Xu K, Driscoll M, Tavernarakis N . Specific aspartyl and calpain proteases are required for neurodegeneration in C. elegans. Nature 2002; 419: 939–944.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Demarchi F, Bertoli C, Copetti T, Tanida I, Brancolini C, Eskelinen EL et al. Calpain is required for macroautophagy in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 2006; 175: 595–605.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Yousefi S, Perozzo R, Schmid I, Ziemiecki A, Schaffner T, Scapozza L et al. Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches autophagy to apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 1124–1132.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Artal-Sanz M, Samara C, Syntichaki P, Tavernarakis N . Lysosomal biogenesis and function is critical for necrotic cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Biol 2006; 173: 231–239.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Yamashima T . Ca2+-dependent proteases in ischemic neuronal death: a conserved ‘calpain-cathepsin cascade’ from nematodes to primates. Cell Calcium 2004; 36: 285–293.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Diskin T, Tal-Or P, Erlich S, Mizrachy L, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E et al. Closed head injury induces upregulation of beclin 1 at the cortical site of injury. J Neurotrauma 2005; 22: 750–762.
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Egami Y, Kiryu-Seo S, Yoshimori T, Kiyama H . Induced expressions of Rab24 GTPase and LC3 in nerve-injured motor neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 337: 1206–1213.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Borsello T, Croquelois K, Hornung JP, Clarke PG . N-methyl-d-aspartate-triggered neuronal death in organotypic hippocampal cultures is endocytic, autophagic and mediated by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. Eur J Neurosci 2003; 18: 473–485.
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Yue Z, Horton A, Bravin M, DeJager PL, Selimi F, Heintz N . A novel protein complex linking the delta 2 glutamate receptor and autophagy: implications for neurodegeneration in lurcher mice. Neuron 2002; 35: 921–933.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Brenner S . The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974; 77: 71–94.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Fire A, Harrison SW, Dixon D . A modular set of lacZ fusion vectors for studying gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene 1990; 93: 189–198.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Kamath RS, Martinez-Campos M, Zipperlen P, Fraser AG, Ahringer J . Effectiveness of specific RNA-mediated interference through ingested double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Biol 2001; 2:RESEARCH0002.
- Berger AJ, Hart AC, Kaplan JM . G alphas-induced neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 1998; 18: 2871–2880.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We thank Stephan Andreas Angermayr, Sampeter Odera, and Evanthia Zaharioudaki for help with RNAi experiments and our colleagues at IMBB for stimulating discussions and comments on the manuscript. Some nematode strains used in this work were provided by the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center, which is funded by the NIH National Center for Research Resources (NCRR), the C. elegans Gene Knockout Project at OMRF (http://www.mutantfactory.ouhsc.edu/), which is part of the International C. elegans Gene Knockout Consortium, and Dr. Shohei Mitani (National Bioresource Project) in Japan. We thank A. Fire for plasmid vectors and J Kaplan for the KP137 strain. This work was funded by grants from EMBO and the EU sixth Framework Programme to NT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Foundation for Research and Technology, Heraklion, 71110, Crete, Greece
C Samara, P Syntichaki & N Tavernarakis
Authors
- C Samara
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - P Syntichaki
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - N Tavernarakis
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toN Tavernarakis.
Additional information
Edited by E Baehrecke
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samara, C., Syntichaki, P. & Tavernarakis, N. Autophagy is required for necrotic cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Death Differ 15, 105–112 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402231
- Received: 12 June 2007
- Revised: 02 August 2007
- Accepted: 20 August 2007
- Published: 28 September 2007
- Issue Date: January 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402231