GraphPlot - Graph plot appearance and behavior - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Main Content
GraphPlot Properties
Graph plot appearance and behavior
GraphPlot properties control the appearance and behavior of plotted graphs. By changing property values, you can modify aspects of the graph display. Use dot notation to refer to a particular object and property:
G = graph([1 1 1 1 5 5 5 5],[2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]); h = plot(G); c = h.EdgeColor; h.EdgeColor = 'k';
Color
NodeColor — Node color
[0 0.4470 0.7410] (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | color name | matrix | 'flat' | 'none'
Node color, specified as one of these values:
'none'— Nodes are not drawn.'flat'— Color of each node depends on the value ofNodeCData.- matrix — Each row is an RGB triplet representing the color of one node. The size of the matrix is
numnodes(G)-by-3. - RGB triplet, hexadecimal color code, or color name — All nodes use the specified color.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7]. - A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.Color Name Short Name RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance "red" "r" [1 0 0] "#FF0000" 
"green" "g" [0 1 0] "#00FF00" 
"blue" "b" [0 0 1] "#0000FF" 
"cyan" "c" [0 1 1] "#00FFFF" 
"magenta" "m" [1 0 1] "#FF00FF" 
"yellow" "y" [1 1 0] "#FFFF00" 
"black" "k" [0 0 0] "#000000" 
"white" "w" [1 1 1] "#FFFFFF" 
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB® uses in many types of plots. RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance ------------------------ ---------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- [0 0.4470 0.7410] "#0072BD" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0 0.4470 0.7410], which appears as dark blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder1.png)
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] "#D95319" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.8500 0.3250 0.0980], which appears as dark orange](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder2.png)
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] "#EDB120" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.9290 0.6940 0.1250], which appears as dark yellow](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder3.png)
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] "#7E2F8E" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4940 0.1840 0.5560], which appears as dark purple](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder4.png)
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] "#77AC30" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4660 0.6740 0.1880], which appears as medium green](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder5.png)
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] "#4DBEEE" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.3010 0.7450 0.9330], which appears as light blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder6.png)
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] "#A2142F" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.6350 0.0780 0.1840], which appears as dark red](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder7.png)
- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
Example: plot(G,'NodeColor','k') creates a graph plot with black nodes.
NodeColorMode — Control how NodeColor is set
'auto' (default) | 'manual'
Control how the NodeColor property is set, specified as one of these values:
'auto'— MATLAB controls the value of theNodeColorproperty by using theSeriesIndexproperty of theGraphPlotobject and theColorOrderproperty of the axes.'manual'— You control the value of theNodeColorproperty manually, either by setting the value of theNodeColorproperty directly on the object, or by including a color in theLineSpecargument when you call a plotting function.
If you change the value of the NodeColor orNodeCData property manually, MATLAB changes the value of the NodeColorMode property to'manual'.
EdgeColor — Edge color
[0 0.4470 0.7410] (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | color name | matrix | 'flat' | 'none'
Edge color, specified as one of these values:
'none'— Edges are not drawn.'flat'— Color of each edge depends on the value ofEdgeCData.- matrix — Each row is an RGB triplet representing the color of one edge. The size of the matrix is
numedges(G)-by-3. - RGB triplet, hexadecimal color code, or color name — All edges use the specified color.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7]. - A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.Color Name Short Name RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance "red" "r" [1 0 0] "#FF0000" 
"green" "g" [0 1 0] "#00FF00" 
"blue" "b" [0 0 1] "#0000FF" 
"cyan" "c" [0 1 1] "#00FFFF" 
"magenta" "m" [1 0 1] "#FF00FF" 
"yellow" "y" [1 1 0] "#FFFF00" 
"black" "k" [0 0 0] "#000000" 
"white" "w" [1 1 1] "#FFFFFF" 
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots. RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance ------------------------ ---------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- [0 0.4470 0.7410] "#0072BD" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0 0.4470 0.7410], which appears as dark blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder1.png)
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] "#D95319" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.8500 0.3250 0.0980], which appears as dark orange](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder2.png)
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] "#EDB120" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.9290 0.6940 0.1250], which appears as dark yellow](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder3.png)
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] "#7E2F8E" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4940 0.1840 0.5560], which appears as dark purple](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder4.png)
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] "#77AC30" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4660 0.6740 0.1880], which appears as medium green](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder5.png)
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] "#4DBEEE" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.3010 0.7450 0.9330], which appears as light blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder6.png)
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] "#A2142F" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.6350 0.0780 0.1840], which appears as dark red](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder7.png)
- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
Example: plot(G,'EdgeColor','r') creates a graph plot with red edges.
EdgeColorMode — Control how EdgeColor is set
'auto' (default) | 'manual'
Control how the EdgeColor property is set, specified as one of these values:
'auto'— MATLAB controls the value of theEdgeColorproperty by using theSeriesIndexproperty of theGraphPlotobject and theColorOrderproperty of the axes.'manual'— You control the value of theEdgeColorproperty manually, either by setting the value of theEdgeColorproperty directly on the object, or by including a color in theLineSpecargument when you call a plotting function.
If you change the value of the EdgeColor orEdgeCData property manually, MATLAB changes the value of the EdgeColorMode property to'manual'.
NodeCData — Color data of node markers
vector
Color data of node markers, specified as a vector with length equal to the number of nodes in the graph. The values in NodeCData map linearly to the colors in the current colormap, resulting in different colors for each node in the plotted graph.
EdgeCData — Color data of edge lines
vector
Color data of edge lines, specified as a vector with length equal to the number of edges in the graph. The values in EdgeCData map linearly to the colors in the current colormap, resulting in different colors for each edge in the plotted graph.
SeriesIndex — Series index
positive whole number | "none"
Series index, specified as a positive whole number or "none". This property is useful for reassigning the node or edge colors of severalGraphPlot objects so that they match each other. By default, theSeriesIndex property of a GraphPlot object is a number that corresponds to its order of creation, starting at 1. MATLAB uses the number to calculate indices for assigning colors when you call plotting functions. The indices refer to the rows of the arrays stored in theColorOrder property of the axes.
A SeriesIndex value of"none" corresponds to a neutral color that does not participate in the indexing scheme. (since R2023b)
MATLAB automatically updates the node and edge colors of theGraphPlot object when you change its SeriesIndex, or when you change the ColorOrder property on the axes. However, the following conditions must be true for the changes to have any effect:
- If
NodeColorModeis'auto', thenSeriesIndexaffects the color of the nodes. - If
EdgeColorModeis'auto', thenSeriesIndexaffects the color of the edges. - The
SeriesIndexproperty of theGraphPlotobject must have a value greater than 0. - The
NextSeriesIndexproperty of theAxesobject must have a value greater than 0.
Node and Edge Styling
Marker — Node marker symbol
'o' (default) | character vector | cell array | string vector
Node marker symbol, specified as one of the values listed in this table, or as a cell array or string vector of such values. The default is to use circular markers for the graph nodes. Specify a cell array of character vectors or string vector to use different markers for each node.
| Marker | Description | Resulting Marker |
|---|---|---|
| "o" | Circle | 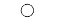 |
| "+" | Plus sign | 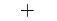 |
| "*" | Asterisk |  |
| "." | Point | 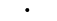 |
| "x" | Cross |  |
| "_" | Horizontal line | 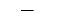 |
| "|" | Vertical line | 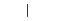 |
| "square" | Square |  |
| "diamond" | Diamond | 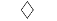 |
| "^" | Upward-pointing triangle |  |
| "v" | Downward-pointing triangle |  |
| ">" | Right-pointing triangle | 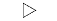 |
| "<" | Left-pointing triangle | 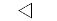 |
| "pentagram" | Pentagram | 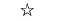 |
| "hexagram" | Hexagram |  |
| "none" | No markers | Not applicable |
Example: '+'
Example: 'diamond'
MarkerSize — Node marker size
positive value | vector
Node marker size, specified as a positive value in point units or as a vector of such values. Specify a vector to use different marker sizes for each node in the graph. The default value of MarkerSize is 4 for graphs with 100 or fewer nodes, and2 for graphs with more than 100 nodes.
Example: 10
LineStyle — Line style
'-' (default) | '--' | ':' | '-.' | 'none' | cell array | string vector
Line style, specified as one of the line styles listed in this table, or as a cell array or string vector of such values. Specify a cell array of character vectors or string vector to use different line styles for each edge.
| Character(s) | Line Style | Resulting Line |
|---|---|---|
| '-' | Solid line | 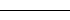 |
| '--' | Dashed line | 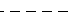 |
| ':' | Dotted line | 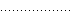 |
| '-.' | Dash-dotted line |  |
| 'none' | No line | No line |
LineWidth — Edge line width
0.5 (default) | positive value | vector
Edge line width, specified as a positive value in point units, or as a vector of such values. Specify a vector to use a different line width for each edge in the graph.
Example: 0.75
EdgeAlpha — Transparency of graph edges
0.5 (default) | scalar value between 0 and 1 inclusive
Transparency of graph edges, specified as a scalar value between 0 and1 inclusive. A value of 1 means fully opaque and0 means completely transparent (invisible).
Example: 0.25
ArrowSize — Arrow size
positive value | vector of positive values
Arrow size, specified as a positive value in point units or as a vector of such values. As a vector, ArrowSize specifies the size of the arrow for each edge in the graph. The default value of ArrowSize is 7 for graphs with 100 or fewer nodes, and 4 for graphs with more than 100 nodes.
ArrowSize only affects directed graphs.
Example: 15
ArrowPosition — Position of arrow along edge
0.5 (default) | scalar | vector
Position of arrow along edge, specified as a value in the range [0 1] or as a vector of such values with length equal to the number of edges. A value near 0 places arrows closer to the source node, and a value near 1 places arrows closer to the target node. The default value is 0.5 so that the arrows are halfway between the source and target nodes.
ArrowPosition only affects directed graphs.
ShowArrows — Toggle display of arrows on directed edges
on/off logical value
Toggle display of arrows on directed edges, specified as 'off' or'on', or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or 0 (false). A value of'on' is equivalent to true, and'off' is equivalent to false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
For directed graphs the default value is 'on' so that arrows are displayed, but you can specify a value of 'off' to hide the arrows on the directed edges. For undirected graphs ShowArrows is always'off'.
Position
XData — x-coordinate of nodes
vector
Note
XData and YData must be specified together so that each node has a valid (x,y) coordinate. Optionally, you can specify ZData for 3-D coordinates.
x-coordinate of nodes, specified as a vector with length equal to the number of nodes in the graph.
YData — y-coordinate of nodes
vector
Note
XData and YData must be specified together so that each node has a valid (x,y) coordinate. Optionally, you can specify ZData for 3-D coordinates.
y-coordinate of nodes, specified as a vector with length equal to the number of nodes in the graph.
ZData — z-coordinate of nodes
vector
Note
XData and YData must be specified together so that each node has a valid (x,y) coordinate. Optionally, you can specify ZData for 3-D coordinates.
z-coordinate of nodes, specified as a vector with length equal to the number of nodes in the graph.
Node and Edge Labels
NodeLabel — Node labels
node IDs (default) | vector | cell array of character vectors
Node labels, specified as a numeric vector or cell array of character vectors. The length of NodeLabel must be equal to the number of nodes in the graph. By defaultNodeLabel is a cell array containing the node IDs for the graph nodes:
- For nodes without names (that is,
G.Nodesdoes not contain aNamevariable), the node labels are the valuesunique(G.Edges.EndNodes)contained in a cell array. - For named nodes, the node labels are
G.Nodes.Name'.
Example: {'A', 'B', 'C'}
Example: [1 2 3]
Example: plot(G,'NodeLabel',G.Nodes.Name) labels the nodes with their names.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | cell
NodeLabelMode — Selection mode for node labels
'auto' (default) | 'manual'
Selection mode for node labels, specified as 'auto' (default) or'manual'. Specify NodeLabelMode as'auto' to populate NodeLabel with the node IDs for the graph nodes (numeric node indices or node names). Specifying NodeLabelMode as 'manual' does not change the values inNodeLabel.
NodeLabelColor — Color of node labels
[0 0 0] (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | color name | matrix
Node label color, specified as one of these values:
- matrix — Each row is an RGB triplet representing the color of one node label. The size of the matrix is
numnodes(G)-by-3. - RGB triplet, hexadecimal color code, or color name — All node labels use the specified color.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7]. - A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.Color Name Short Name RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance "red" "r" [1 0 0] "#FF0000" 
"green" "g" [0 1 0] "#00FF00" 
"blue" "b" [0 0 1] "#0000FF" 
"cyan" "c" [0 1 1] "#00FFFF" 
"magenta" "m" [1 0 1] "#FF00FF" 
"yellow" "y" [1 1 0] "#FFFF00" 
"black" "k" [0 0 0] "#000000" 
"white" "w" [1 1 1] "#FFFFFF" 
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots. RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance ------------------------ ---------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- [0 0.4470 0.7410] "#0072BD" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0 0.4470 0.7410], which appears as dark blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder1.png)
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] "#D95319" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.8500 0.3250 0.0980], which appears as dark orange](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder2.png)
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] "#EDB120" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.9290 0.6940 0.1250], which appears as dark yellow](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder3.png)
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] "#7E2F8E" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4940 0.1840 0.5560], which appears as dark purple](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder4.png)
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] "#77AC30" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4660 0.6740 0.1880], which appears as medium green](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder5.png)
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] "#4DBEEE" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.3010 0.7450 0.9330], which appears as light blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder6.png)
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] "#A2142F" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.6350 0.0780 0.1840], which appears as dark red](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder7.png)
- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
Example: plot(G,'NodeLabel',C,'NodeLabelColor','m') creates a graph plot with magenta node labels.
EdgeLabel — Edge labels
{} (default) | vector | cell array of character vectors
Edge labels, specified as a numeric vector or cell array of character vectors. The length of EdgeLabel must be equal to the number of edges in the graph. By defaultEdgeLabel is an empty cell array (no edge labels are displayed).
Example: {'A', 'B', 'C'}
Example: [1 2 3]
Example: plot(G,'EdgeLabels',G.Edges.Weight) labels the graph edges with their weights.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | cell
EdgeLabelMode — Selection mode for edge labels
'manual' (default) | 'auto'
Selection mode for edge labels, specified as 'manual' (default) or'auto'. Specify EdgeLabelMode as'auto' to populate EdgeLabel with the edge weights inG.Edges.Weight (if available), or the edge indicesG.Edges(k,:) (if no weights are available). SpecifyingEdgeLabelMode as 'manual' does not change the values inEdgeLabel.
EdgeLabelColor — Color of edge labels
[0 0 0] (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | color name | matrix
Edge label color, specified as one of these values:
- matrix — Each row is an RGB triplet representing the color of one edge label. The size of the matrix is
numedges(G)-by-3. - RGB triplet, hexadecimal color code, or color name — All edge labels use the specified color.
RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes are useful for specifying custom colors.- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1]; for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7]. - A hexadecimal color code is a character vector or a string scalar that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Thus, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.Color Name Short Name RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance "red" "r" [1 0 0] "#FF0000" 
"green" "g" [0 1 0] "#00FF00" 
"blue" "b" [0 0 1] "#0000FF" 
"cyan" "c" [0 1 1] "#00FFFF" 
"magenta" "m" [1 0 1] "#FF00FF" 
"yellow" "y" [1 1 0] "#FFFF00" 
"black" "k" [0 0 0] "#000000" 
"white" "w" [1 1 1] "#FFFFFF" 
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots. RGB Triplet Hexadecimal Color Code Appearance ------------------------ ---------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- [0 0.4470 0.7410] "#0072BD" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0 0.4470 0.7410], which appears as dark blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder1.png)
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] "#D95319" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.8500 0.3250 0.0980], which appears as dark orange](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder2.png)
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] "#EDB120" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.9290 0.6940 0.1250], which appears as dark yellow](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder3.png)
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] "#7E2F8E" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4940 0.1840 0.5560], which appears as dark purple](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder4.png)
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] "#77AC30" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.4660 0.6740 0.1880], which appears as medium green](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder5.png)
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] "#4DBEEE" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.3010 0.7450 0.9330], which appears as light blue](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder6.png)
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] "#A2142F" ![Sample of RGB triplet [0.6350 0.0780 0.1840], which appears as dark red](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colororder7.png)
- An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
Example: plot(G,'EdgeLabel',C,'EdgeLabelColor','m') creates a graph plot with magenta edge labels.
Interpreter — Interpretation of text characters
'tex' (default) | 'latex' | 'none'
Interpretation of text characters, specified as one of these values:
'tex'— Interpret characters using a subset of TeX markup.'latex'— Interpret characters using LaTeX markup.'none'— Display literal characters.
TeX Markup
By default, MATLAB supports a subset of TeX markup. Use TeX markup to add superscripts and subscripts, modify the font type and color, and include special characters in the text.
Modifiers remain in effect until the end of the text. Superscripts and subscripts are an exception because they modify only the next character or the characters within the curly braces. When you set the interpreter to 'tex', the supported modifiers are as follows.
| Modifier | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ^{ } | Superscript | 'text^{superscript}' |
| _{ } | Subscript | 'text_{subscript}' |
| \bf | Bold font | '\bf text' |
| \it | Italic font | '\it text' |
| \sl | Oblique font (usually the same as italic font) | '\sl text' |
| \rm | Normal font | '\rm text' |
| \fontname{specifier} | Font name — Replace_specifier_ with the name of a font family. You can use this in combination with other modifiers. | '\fontname{Courier} text' |
| \fontsize{specifier} | Font size —Replace_specifier_ with a numeric scalar value in point units. | '\fontsize{15} text' |
| \color{specifier} | Font color — Replace_specifier_ with one of these colors: red, green,yellow, magenta,blue, black,white, gray,darkGreen, orange, orlightBlue. | '\color{magenta} text' |
| \color[rgb]{specifier} | Custom font color — Replace_specifier_ with a three-element RGB triplet. | '\color[rgb]{0,0.5,0.5} text' |
This table lists the supported special characters for the'tex' interpreter.
| Character Sequence | Symbol | Character Sequence | Symbol | Character Sequence | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| \alpha | α | \upsilon | υ | \sim | ~ |
| \angle | ∠ | \phi | ϕ | \leq | ≤ |
| \ast | * | \chi | χ | \infty | ∞ |
| \beta | β | \psi | ψ | \clubsuit | ♣ |
| \gamma | γ | \omega | ω | \diamondsuit | ♦ |
| \delta | δ | \Gamma | Γ | \heartsuit | ♥ |
| \epsilon | ϵ | \Delta | Δ | \spadesuit | ♠ |
| \zeta | ζ | \Theta | Θ | \leftrightarrow | ↔ |
| \eta | η | \Lambda | Λ | \leftarrow | ← |
| \theta | θ | \Xi | Ξ | \Leftarrow | ⇐ |
| \vartheta | ϑ | \Pi | Π | \uparrow | ↑ |
| \iota | ι | \Sigma | Σ | \rightarrow | → |
| \kappa | κ | \Upsilon | ϒ | \Rightarrow | ⇒ |
| \lambda | λ | \Phi | Φ | \downarrow | ↓ |
| \mu | µ | \Psi | Ψ | \circ | º |
| \nu | ν | \Omega | Ω | \pm | ± |
| \xi | ξ | \forall | ∀ | \geq | ≥ |
| \pi | π | \exists | ∃ | \propto | ∝ |
| \rho | ρ | \ni | ∍ | \partial | ∂ |
| \sigma | σ | \cong | ≅ | \bullet | • |
| \varsigma | ς | \approx | ≈ | \div | ÷ |
| \tau | τ | \Re | ℜ | \neq | ≠ |
| \equiv | ≡ | \oplus | ⊕ | \aleph | ℵ |
| \Im | ℑ | \cup | ∪ | \wp | ℘ |
| \otimes | ⊗ | \subseteq | ⊆ | \oslash | ∅ |
| \cap | ∩ | \in | ∈ | \supseteq | ⊇ |
| \supset | ⊃ | \lceil | ⌈ | \subset | ⊂ |
| \int | ∫ | \cdot | · | \o | ο |
| \rfloor | ⌋ | \neg | ¬ | \nabla | ∇ |
| \lfloor | ⌊ | \times | x | \ldots | ... |
| \perp | ⊥ | \surd | √ | \prime | ´ |
| \wedge | ∧ | \varpi | ϖ | \0 | ∅ |
| \rceil | ⌉ | \rangle | 〉 | \mid | | |
| \vee | ∨ | \langle | 〈 | \copyright | © |
LaTeX Markup
To use LaTeX markup, set the Interpreter property to'latex'. Use dollar symbols around the text, for example, use'$\int_1^{20} x^2 dx$' for inline mode or '$$\int_1^{20} x^2 dx$$' for display mode.
The displayed text uses the default LaTeX font style. The FontName,FontWeight, and FontAngle properties do not have an effect. To change the font style, use LaTeX markup.
The maximum size of the text that you can use with the LaTeX interpreter is 1200 characters.
For more information about the LaTeX system, see The LaTeX Project website at https://www.latex-project.org/.
Font
NodeFontName — Font name for node labels
'Helvetica' (default) | supported font name | 'FixedWidth'
Font name for node labels, specified as a supported font name or'FixedWidth'. For labels to display and print properly, you must choose a font that your system supports. The default font depends on the specific operating system and locale. For example, Windows® and Linux® systems in English localization use the Helvetica font by default.
To use a fixed-width font that looks good in any locale, specify'FixedWidth'.
Example: 'Cambria'
NodeFontSize — Font size for node labels
positive number | vector of positive numbers
Font size for node labels, specified as a positive number or a vector of positive numbers. If NodeFontSize is a vector, then each element specifies the font size of one node label. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale.
NodeFontWeight — Thickness of text in node labels
'normal' (default) | 'bold' | vector | cell array
Thickness of text in node labels, specified as 'normal','bold', or as a string vector or cell array of character vectors specifying 'normal' or 'bold' for each node.
'bold'— Thicker character outlines than normal'normal'— Normal weight as defined by the particular font
Not all fonts have a bold font weight.
Data Types: cell | char | string
NodeFontAngle — Character slant of text in node labels
'normal' (default) | 'italic' | vector | cell array
Character slant of text in node labels, specified as 'normal','italic', or as a string vector or cell array of character vectors specifying 'normal' or 'italic' for each node.
'italic'— Slanted characters'normal'— No character slant
Not all fonts have both font styles.
Data Types: cell | char | string
EdgeFontName — Font name for edge labels
'Helvetica' (default) | supported font name | 'FixedWidth'
Font name for edge labels, specified as a supported font name or'FixedWidth'. For labels to display and print properly, you must choose a font that your system supports. The default font depends on the specific operating system and locale. For example, Windows and Linux systems in English localization use the Helvetica font by default.
To use a fixed-width font that looks good in any locale, specify'FixedWidth'.
Example: 'Cambria'
EdgeFontSize — Font size for edge labels
positive number | vector of positive numbers
Font size for edge labels, specified as a positive number or a vector of positive numbers. If EdgeFontSize is a vector, then each element specifies the font size of one edge label. The default font size depends on the specific operating system and locale.
EdgeFontWeight — Thickness of text in edge labels
'normal' (default) | 'bold' | vector | cell array
Thickness of text in edge labels, specified as 'normal','bold', or as a string vector or cell array of character vectors specifying 'normal' or 'bold' for each edge.
'bold'— Thicker character outlines than normal'normal'— Normal weight as defined by the particular font
Not all fonts have a bold font weight.
Data Types: cell | char | string
EdgeFontAngle — Character slant of text in edge labels
'normal' (default) | 'italic' | vector | cell array
Character slant of text in edge labels, specified as 'normal','italic', or as a string vector or cell array of character vectors specifying 'normal' or 'italic' for each edge.
'italic'— Slanted characters'normal'— No character slant
Not all fonts have both font styles.
Data Types: cell | char | string
Legend
DisplayName — Text used by legend
'' (default) | character vector
Text used by the legend, specified as a character vector. The text appears next to an icon of the GraphPlot.
Example: 'Text Description'
For multiline text, create the character vector using sprintf with the new line character \n.
Example: sprintf('line one\nline two')
Alternatively, you can specify the legend text using the legend function.
- If you specify the text as an input argument to the legend function, then the legend uses the specified text and sets the
DisplayNameproperty to the same value. - If you do not specify the text as an input argument to the legend function, then the legend uses the text in the
DisplayNameproperty. If theDisplayNameproperty does not contain any text, then the legend generates a character vector. The character vector has the form'dataN', whereNis the number assigned to the GraphPlot object based on its location in the list of legend entries.
If you edit interactively the character vector in an existing legend, then MATLAB updates the DisplayName property to the edited character vector.
Annotation — Legend icon display style
Annotation object
This property is read-only.
Legend icon display style, returned as an Annotation object. Use this object to include or exclude the GraphPlot from a legend.
- Query the
Annotationproperty to get theAnnotationobject. - Query the
LegendInformationproperty of theAnnotationobject to get theLegendEntryobject. - Specify the
IconDisplayStyleproperty of theLegendEntryobject to one of these values:'on'— Include the GraphPlot object in the legend as one entry (default).'off'— Do not include the GraphPlot object in the legend.'children'— Include only children of the GraphPlot object as separate entries in the legend.
If a legend already exists and you change theIconDisplayStyle setting, then you must call legend to update the display.
Interactivity
DataTipTemplate — Data tip content
DataTipTemplate object
Data tip content, specified as a DataTipTemplate object. You can control the content that appears in a data tip by modifying the properties of the underlying DataTipTemplate object. For a list of properties, seeDataTipTemplate Properties.
For an example of modifying data tips, see Create Custom Data Tips.
Note
The DataTipTemplate object is not returned byfindobj or findall, and it is not copied by copyobj.
State of visibility, specified as "on" or "off", or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or0 (false). A value of "on" is equivalent to true, and "off" is equivalent tofalse. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
"on"— Display the object."off"— Hide the object without deleting it. You still can access the properties of an invisible object.
Context menu, specified as a ContextMenu object. Use this property to display a context menu when you right-click the object. Create the context menu using the uicontextmenu function.
Note
If the PickableParts property is set to'none' or if the HitTest property is set to 'off', then the context menu does not appear.
Selection state, specified as 'on' or 'off', or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or0 (false). A value of 'on' is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent tofalse. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
'on'— Selected. If you click the object when in plot edit mode, then MATLAB sets itsSelectedproperty to'on'. If theSelectionHighlightproperty also is set to'on', then MATLAB displays selection handles around the object.'off'— Not selected.
Display of selection handles when selected, specified as 'on' or'off', or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or 0 (false). A value of 'on' is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
'on'— Display selection handles when theSelectedproperty is set to'on'.'off'— Never display selection handles, even when theSelectedproperty is set to'on'.
Callbacks
ButtonDownFcn — Mouse-click callback
'' (default) | function handle | cell array | character vector
Mouse-click callback, specified as one of these values:
- Function handle
- Cell array containing a function handle and additional arguments
- Character vector that is a valid MATLAB command or function, which is evaluated in the base workspace (not recommended)
Use this property to execute code when you click the GraphPlot. If you specify this property using a function handle, then MATLAB passes two arguments to the callback function when executing the callback:
- The GraphPlot object — You can access properties of the GraphPlot object from within the callback function.
- Event data — This argument is empty for this property. Replace it with the tilde character (
~) in the function definition to indicate that this argument is not used.
For more information on how to use function handles to define callback functions, see Create Callbacks for Graphics Objects.
Note
If the PickableParts property is set to 'none' or if the HitTest property is set to 'off', then this callback does not execute.
Example: @myCallback
Example: {@myCallback,arg3}
CreateFcn — Creation callback
'' (default) | function handle | cell array | character vector
Creation callback, specified as one of these values:
- Function handle
- Cell array containing a function handle and additional arguments
- Character vector that is a valid MATLAB command or function, which is evaluated in the base workspace (not recommended)
Use this property to execute code when you create the GraphPlot. Setting the CreateFcn property on an existing GraphPlot has no effect. You must define a default value for this property, or define this property using a Name,Value pair during GraphPlot creation. MATLAB executes the callback after creating the GraphPlot and setting all of its properties.
If you specify this callback using a function handle, then MATLAB passes two arguments to the callback function when executing the callback:
- The GraphPlot object — You can access properties of the GraphPlot object from within the callback function. You also can access the GraphPlot object through the
CallbackObjectproperty of the root, which can be queried using thegcbofunction. - Event data — This argument is empty for this property. Replace it with the tilde character (
~) in the function definition to indicate that this argument is not used.
For more information on how to use function handles to define callback functions, see Create Callbacks for Graphics Objects.
Example: @myCallback
Example: {@myCallback,arg3}
DeleteFcn — Deletion callback
'' (default) | function handle | cell array | character vector
Deletion callback, specified as one of these values:
- Function handle
- Cell array containing a function handle and additional arguments
- Character vector that is a valid MATLAB command or function, which is evaluated in the base workspace (not recommended)
Use this property to execute code when you delete the GraphPlot. MATLAB executes the callback before destroying the GraphPlot so that the callback can access its property values.
If you specify this callback using a function handle, then MATLAB passes two arguments to the callback function when executing the callback:
- The GraphPlot object — You can access properties of the GraphPlot object from within the callback function. You also can access the GraphPlot object through the
CallbackObjectproperty of the root, which can be queried using thegcbofunction. - Event data — This argument is empty for this property. Replace it with the tilde character (
~) in the function definition to indicate that this argument is not used.
For more information on how to use function handles to define callback functions, see Create Callbacks for Graphics Objects.
Example: @myCallback
Example: {@myCallback,arg3}
Callback Execution Control
Callback interruption, specified as 'on' or 'off', or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or0 (false). A value of 'on' is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent tofalse. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
This property determines if a running callback can be interrupted. There are two callback states to consider:
- The running callback is the currently executing callback.
- The interrupting callback is a callback that tries to interrupt the running callback.
MATLAB determines callback interruption behavior whenever it executes a command that processes the callback queue. These commands include drawnow, figure, uifigure, getframe, waitfor, and pause.
If the running callback does not contain one of these commands, then no interruption occurs. MATLAB first finishes executing the running callback, and later executes the interrupting callback.
If the running callback does contain one of these commands, then theInterruptible property of the object that owns the running callback determines if the interruption occurs:
- If the value of
Interruptibleis'off', then no interruption occurs. Instead, theBusyActionproperty of the object that owns the interrupting callback determines if the interrupting callback is discarded or added to the callback queue. - If the value of
Interruptibleis'on', then the interruption occurs. The next time MATLAB processes the callback queue, it stops the execution of the running callback and executes the interrupting callback. After the interrupting callback completes, MATLAB then resumes executing the running callback.
Note
Callback interruption and execution behave differently in these situations:
- If the interrupting callback is a
DeleteFcn,CloseRequestFcn, orSizeChangedFcncallback, then the interruption occurs regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value. - If the running callback is currently executing the
waitforfunction, then the interruption occurs regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value. - If the interrupting callback is owned by a
Timerobject, then the callback executes according to schedule regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value.
Note
When an interruption occurs, MATLAB does not save the state of properties or the display. For example, the object returned by the gca or gcf command might change when another callback executes.
BusyAction — Callback queuing
'queue' (default) | 'cancel'
Callback queuing specified as 'queue' or 'cancel'. The BusyAction property determines how MATLAB handles the execution of interrupting callbacks.
Note
There are two callback states to consider:
- The running callback is the currently executing callback.
- The interrupting callback is a callback that tries to interrupt the running callback.
Whenever MATLAB invokes a callback, that callback attempts to interrupt a running callback. TheInterruptible property of the object owning the running callback determines if interruption is allowed. If interruption is not allowed, then theBusyAction property of the object owning the interrupting callback determines if it is discarded or put in the queue.
If the ButtonDownFcn callback of the GraphPlot tries to interrupt a running callback that cannot be interrupted, then theBusyAction property determines if it is discarded or put in the queue. Specify the BusyAction property as one of these values:
'queue'— Put the interrupting callback in a queue to be processed after the running callback finishes execution. This is the default behavior.'cancel'— Discard the interrupting callback.
PickableParts — Ability to capture mouse clicks
'visible' (default) | 'none'
Ability to capture mouse clicks, specified as one of these values:
'visible'— Can capture mouse clicks only when visible. TheVisibleproperty must be set to'on'. TheHitTestproperty determines if the GraphPlot responds to the click or if an ancestor does.'none'— Cannot capture mouse clicks. Clicking the GraphPlot passes the click to the object below it in the current view of the figure window. TheHitTestproperty of the GraphPlot has no effect.
Response to captured mouse clicks, specified as 'on' or'off', or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or 0 (false). A value of 'on' is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
'on'— Trigger theButtonDownFcncallback of theGraphPlotobject. If you have defined theContextMenuproperty, then invoke the context menu.'off'— Trigger the callbacks for the nearest ancestor of theGraphPlotobject that meets one of these conditions:HitTestproperty is set to'on'.PickablePartsproperty is set to a value that enables the ancestor to capture mouse clicks.
Note
The PickableParts property determines if the GraphPlot object can capture mouse clicks. If it cannot, then the HitTest property has no effect.
This property is read-only.
Deletion status, returned as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
MATLAB sets the BeingDeleted property to'on' when the DeleteFcn callback begins execution. The BeingDeleted property remains set to'on' until the component object no longer exists.
Check the value of the BeingDeleted property to verify that the object is not about to be deleted before querying or modifying it.
Parent/Child
Parent — Parent of GraphPlot
axes object | group object | transform object
Parent of GraphPlot, specified as an axes, group, or transform object.
Children, returned as an empty GraphicsPlaceholder array or aDataTip object array. Use this property to view a list of data tips that are plotted on the chart.
You cannot add or remove children using the Children property. To add a child to this list, set the Parent property of theDataTip object to the chart object.
HandleVisibility — Visibility of object handle
'on' (default) | 'off' | 'callback'
Visibility of GraphPlot object handle in theChildren property of the parent, specified as one of these values:
'on'— The GraphPlot object handle is always visible.'off'— The GraphPlot object handle is invisible at all times. This option is useful for preventing unintended changes to the UI by another function. Set theHandleVisibilityto'off'to temporarily hide the handle during the execution of that function.'callback'— The GraphPlot object handle is visible from within callbacks or functions invoked by callbacks, but not from within functions invoked from the command line. This option blocks access to the GraphPlot at the command-line, but allows callback functions to access it.
If the GraphPlot object is not listed in theChildren property of the parent, then functions that obtain object handles by searching the object hierarchy or querying handle properties cannot return it. This includes get, findobj, gca, gcf, gco, newplot, cla, clf, and close.
Hidden object handles are still valid. Set the rootShowHiddenHandles property to 'on' to list all object handles regardless of their HandleVisibility property setting.
Identifiers
Type — Type of graphics object
'graphplot'
This property is read-only.
Type of graphics object, returned as 'graphplot'. Use this property to find all objects of a given type within a plotting hierarchy, such as searching for the type using findobj.
Tag — Tag to associate with GraphPlot
'' (default) | character vector
Tag to associate with the GraphPlot, specified as a character vector. Tags provide a way to identify graphics objects. Use this property to find all objects with a specific tag within a plotting hierarchy, for example, searching for the tag using findobj.
Example: 'January Data'
Data Types: char
UserData — Data to associate with GraphPlot
[] (default) | scalar, vector, or matrix | cell array | character array | table | structure
Data to associate with the GraphPlot object, specified as a scalar, vector, matrix, cell array, character array, table, or structure. MATLAB does not use this data.
To associate multiple sets of data or to attach a field name to the data, use thegetappdata and setappdata functions.
Example: 1:100
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | struct | table | cell
Version History
Introduced in R2015b
R2023b: Opt out of automatic color selection with SeriesIndex="none"
Opt out of automatic color selection for GraphPlot objects by setting theSeriesIndex property to "none". When you specify"none", the GraphPlot object has a neutral color.
To enable automatic color selection again, set the SeriesIndex property to a positive whole number.
R2020a: Control automatic color selection with the SeriesIndex property
Control how GraphPlot objects vary in color by setting theSeriesIndex property. This property is useful when you want to match the colors of different objects in the axes.
R2020a: UIContextMenu property is not recommended
Starting in R2020a, using the UIContextMenu property to assign a context menu to a graphics object or UI component is not recommended. Use theContextMenu property instead. The property values are the same.
There are no plans to remove support for the UIContextMenu property at this time. However, the UIContextMenu property no longer appears in the list returned by calling the get function on a graphics object or UI component.