fixedWidthImportOptions - Import options object for fixed-width text files - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Import options object for fixed-width text files
Description
A FixedWidthImportOptions object enables you to specify how MATLAB® imports fixed-width tabular data from text files. The object contains properties that control the data import process, including the handling of errors and missing data.
Creation
You can create a FixedWidthImportOptions object using either thefixedWidthImportOptions function (described here) or thedetectImportOptions function:
- Use
fixedWidthImportOptionsto define the import properties based on your import requirements. - Use
detectImportOptionsto detect and populate the import properties based on the contents of the fixed-width text file specified infilename.
opts = detectImportOptions(filename)
Syntax
Description
opts = fixedWidthImportOptions creates aFixedWidthImportOptions object with one variable.
opts = fixedWidthImportOptions('NumVariables',[numVars](#bvmdw9y-1%5Fsep%5Fmw%5Ff5acc160-778c-42ed-a7f2-be23ca93c208)) creates the object with the number of variables specified innumVars.
opts = fixedWidthImportOptions(___,`Name,Value`) specifies additional properties forFixedWidthImportOptions object using one or more name-value pair arguments.
Input Arguments
numVars — Number of variables
positive scalar integer
Number of variables, specified as a positive scalar integer.
Properties
Variable Properties
Variable names, specified as a cell array of character vectors or string array. TheVariableNames property contains the names to use when importing variables.
If the data contains N variables, but no variable names are specified, then the VariableNames property contains{'Var1','Var2',...,'VarN'}.
To support invalid MATLAB identifiers as variable names, such as variable names containing spaces and non-ASCII characters, set the value of VariableNamingRule to'preserve'.
Example: opts.VariableNames returns the current (detected) variable names.
Example: opts.VariableNames(3) = {'Height'} changes the name of the third variable to Height.
Data Types: char | string | cell
VariableNamingRule — Flag to preserve variable names
"modify" (default) | "preserve"
Flag to preserve variable names, specified as either "modify" or"preserve".
"modify"— Convert invalid variable names (as determined by the isvarname function) to valid MATLAB identifiers."preserve"— Preserve variable names that are not valid MATLAB identifiers such as variable names that include spaces and non-ASCII characters.
Starting in R2019b, variable names and row names can include any characters, including spaces and non-ASCII characters. Also, they can start with any characters, not just letters. Variable and row names do not have to be valid MATLAB identifiers (as determined by the isvarname function). To preserve these variable names and row names, set the value of VariableNamingRule to "preserve". Variable names are not refreshed when the value of VariableNamingRule is changed from "modify" to "preserve".
Data Types: char | string
Field widths of variables in a fixed-width text file, specified as a vector of positive integer values. Each positive integer in the vector corresponds to the number of characters in a field that makes up the variable. The VariableWidths property contains an entry corresponding to each variable specified in theVariableNames property.
Data type of variable, specified as a cell array of character vectors, or string array containing a set of valid data type names. The VariableTypes property designates the data types to use when importing variables.
To update the VariableTypes property, use the setvartype function.
Example: opts.VariableTypes returns the current variable data types.
Example: opts = setvartype(opts,'Height',{'double'}) changes the data type of the variable Height todouble.
Subset of variables to import, specified as a character vector, string scalar, cell array of character vectors, string array or an array of numeric indices.
SelectedVariableNames must be a subset of names contained in the VariableNames property. By default, SelectedVariableNames contains all the variable names from the VariableNames property, which means that all variables are imported.
Use the SelectedVariableNames property to import only the variables of interest. Specify a subset of variables using the SelectedVariableNames property and use readtable to import only that subset.
To support invalid MATLAB identifiers as variable names, such as variable names containing spaces and non-ASCII characters, set the value ofVariableNamingRule to'preserve'.
Example: opts.SelectedVariableNames = {'Height','LastName'} selects only two variables, Height and LastName, for the import operation.
Example: opts.SelectedVariableNames = [1 5] selects only two variables, the first variable and the fifth variable, for the import operation.
Example: T = readtable(filename,opts) returns a table containing only the variables specified in the SelectedVariableNames property of the opts object.
Data Types: uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | char | string | cell
Type specific variable import options, returned as an array of variable import options objects. The array contains an object corresponding to each variable specified in the VariableNames property. Each object in the array contains properties that support the importing of data with a specific data type.
Variable options support these data types: numeric, text, logical, datetime, or categorical.
To query the current (or detected) options for a variable, use the getvaropts function.
To set and customize options for a variable, use the setvaropts function.
Example: opts.VariableOptions returns a collection of VariableImportOptions objects, one corresponding to each variable in the data.
Example: getvaropts(opts,'Height') returns the VariableImportOptions object for the Height variable.
Example: opts = setvaropts(opts,'Height','FillValue',0) sets the FillValue property for the variable Height to 0.
Location Properties
Data location, specified as a positive scalar integer or aN-by-2 array of positive scalar integers. Specify DataLines using one of these forms.
| Specify as | Description |
|---|---|
| n | Specify the first line that contains the data. Specifying the value using n sets the value of DataLines property to [n inf]. The importing function reads all rows between n and the end-of-file. n must be a positive integer greater than zero. |
| [n1 n2] | Specify the line range that contains the data. n1 is the first line that contains the data and the n2 is the last line that contains the data.Values in the array [n1 n2] must be nonzero positive integers andn2 must be greater thann1. |
| [n1 n2; n3 n4;...] | Specify multiple line ranges to read with an N-by-2 array containingN different line ranges. A valid array of multiple line ranges must: Specify line ranges in an increasing order, that is the first line range specified in the array appears in the file before the other line ranges.Contain only nonoverlapping line ranges. When specifying multiple line ranges, useInf only when specifying the end of the last line range in the array. For example, [1 3; 5 6; 8 Inf]. |
Example: opts.DataLines = 5 sets the DataLines property to the value [5 inf]. Read all rows of data starting from row 5 to the end-of-file.
Example: opts.DataLines = [2 6] sets the property to read lines2 through 6.
Example: opts.DataLines = [1 3; 5 6; 8 inf] sets the property to read rows 1, 2, 3,5, 6, and all rows between8, and the end-of-file.
Data Types: single | double | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Row names location, specified as a positive scalar integer. The RowNamesColumn property specifies the location of the column containing the row names.
If RowNamesColumn is specified as 0, then do not import the row names. Otherwise, import the row names from the specified column.
Example: opts.RowNamesColumn = 2;
Data Types: single | double | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Variable names location, specified as a positive scalar integer. The VariableNamesLine property specifies the line number where variable names are located.
If VariableNamesLine is specified as 0, then do not import the variable names. Otherwise, import the variable names from the specified line.
Example: opts.VariableNamesLine = 6;
Data Types: single | double | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Variable description location, specified as a positive scalar integer. The VariableDescriptionsLine property specifies the line number where variable descriptions are located.
If VariableDescriptionsLine is specified as 0, then do not import the variable descriptions. Otherwise, import the variable descriptions from the specified line.
Example: opts.VariableDescriptionsLine = 7;
Data Types: single | double | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Variable units location, specified as a positive scalar integer. The VariableUnitsLine property specifies the line number where variable units are located.
If VariableUnitsLine is specified as 0, then do not import the variable units. Otherwise, import the variable units from the specified line.
Example: opts.VariableUnitsLine = 8;
Data Types: single | double | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Delimited Text Properties
Characters to treat as white space, specified as a character vector or string scalar containing one or more characters.
Example: 'Whitespace',' _'
Example: 'Whitespace','?!.,'
End-of-line characters, specified as a string array, character vector, or cell array of character vectors.
Example: "LineEnding","\n"
Example: "LineEnding","\r\n"
Example: "LineEnding",["\b",":"]
Style of comments, specified as a string array, character vector, or cell array of character vectors. For single- and multi-line comments, the starting identifier must be the first non-white-space character. For single-line comments, specify a single identifier to treat lines starting with the identifier as comments. For multi-line comments, lines from the starting (first) identifier to the ending (second) identifier are treated as comments. No more than two character vectors of identifiers can be specified.
For example, to ignore the line following a percent symbol as the first non-white-space character, specify CommentStyle as"%".
Example: "CommentStyle",["/*"]
Example: "CommentStyle",["/*","*/"]
Character encoding scheme associated with the file, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'Encoding' and 'system' or a standard character encoding scheme name.
When you do not specify any encoding, the function uses automatic character set detection to determine the encoding when reading the file.
Example: 'Encoding','system' uses the system default encoding.
Data Types: char | string
Replacement Rules
Procedure to handle partial fields in the data, specified as one of the values in this table.
| Partial Field Rule | Behavior |
|---|---|
| 'keep' | Keep the partial field data and convert the text to the appropriate data type.In some cases, when the importing function is unable to interpret the partial data, a conversion error might occur. |
| 'fill' | Replace missing data with the contents of the FillValue property.The FillValue property is specified in the VariableImportOptions object of the variable being imported. For more information on accessing the FillValue property, see getvaropts. |
| 'omitrow' | Omit rows that contain partial data. |
| 'omitvar' | Omit variables that contain partial data. |
| 'wrap' | Begin reading the next line of characters. |
| 'error' | Display an error message and abort the import operation. |
Example: opts.PartialFieldRule = 'keep';
Data Types: char | string
Procedure to handle empty lines in the data, specified as 'skip', 'read', or 'error'. The importing function interprets white space as empty.
| Empty Line Rule | Behavior |
|---|---|
| 'skip' | Skip the empty lines. |
| 'read' | Import the empty lines. The importing function parses the empty line using the values specified in VariableWidths, VariableOptions, MissingRule, and other relevant properties, such as Whitespace. |
| 'error' | Display an error message and abort the import operation. |
Example: opts.EmptyLineRule = 'skip';
Data Types: char | string
Procedure to manage missing data, specified as one of the values in this table.
| Missing Rule | Behavior |
|---|---|
| 'fill' | Replace missing data with the contents of the FillValue property.The FillValue property is specified in the VariableImportOptions object of the variable being imported. For more information on accessing theFillValue property, see setvaropts. |
| 'error' | Stop importing and display an error message showing the missing record and field. |
| 'omitrow' | Omit rows that contain missing data. |
| 'omitvar' | Omit variables that contain missing data. |
Example: opts.MissingRule = 'omitrow';
Data Types: char | string
Procedure to handle import errors, specified as one of the values in this table.
| Import Error Rule | Behavior |
|---|---|
| 'fill' | Replace the data where the error occurred with the contents of theFillValue property.TheFillValue property is specified in theVariableImportOptions object of the variable being imported. For more information on accessing theFillValue property, see setvaropts. |
| 'error' | Stop importing and display an error message showing the error-causing record and field. |
| 'omitrow' | Omit rows where errors occur. |
| 'omitvar' | Omit variables where errors occur. |
Example: opts.ImportErrorRule = 'omitvar';
Data Types: char | string
Procedure to handle extra columns in the data, specified as one of the values in this table.
| Extra Columns Rule | Behavior |
|---|---|
| 'addvars' | To import extra columns, create new variables. If there are N extra columns, then import new variables as 'ExtraVar1', 'ExtraVar2',..., 'ExtraVarN'. Extra columns of data are imported as if their VariableTypes arechar. |
| 'ignore' | Ignore the extra columns of data. |
| 'wrap' | Wrap the extra columns of data to new records. This action does not change the number of variables. |
| 'error' | Display an error message and abort the import operation. |
Data Types: char | string
Object Functions
Examples
Define Import Options Object to Read Fixed-Width Text File
Examine a fixed-width formatted text file, initialize an import options object, and use the object to import the table from the text file.
Load and Preview Fixed-Width Text File
Load the file fixed_width_patients_subset_perfect.txt and preview its contents in a text editor. The screen shot shows that the file contains fixed-width formatted data.
filename = 'fixed_width_patients_subset_perfect.txt';
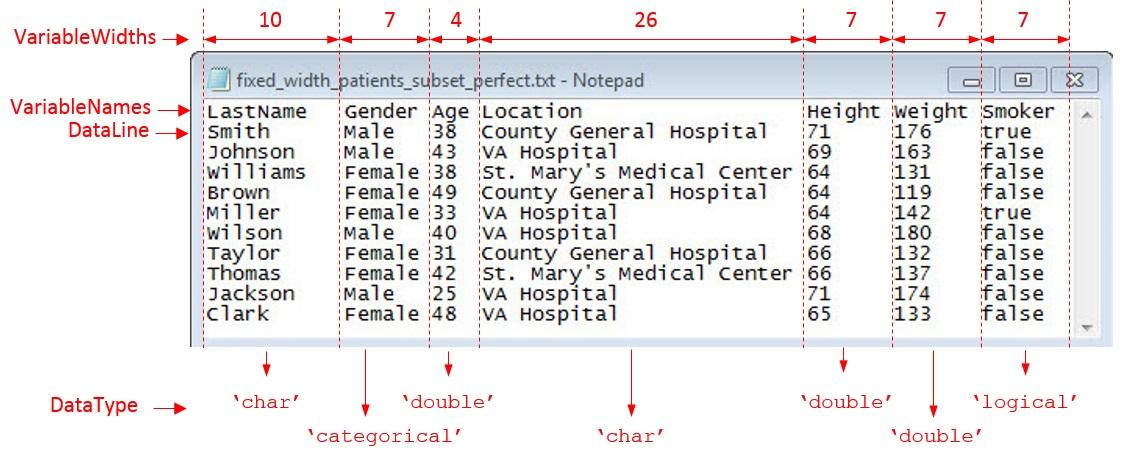
Examine and Extract Properties of Fixed-Width File
The fixed-width text file has tabular data organized by starting location, number of variables, variable names, and variable widths. Capture these properties and the desired data type for the variables.
DataStartLine = 2;
NumVariables = 7;
VariableNames = {'LastName','Gender','Age','Location','Height',...
'Weight','Smoker'};
VariableWidths = [ 10, 7, 4, 26, 7, ...
7, 7 ] ;
DataType = {'char','categorical','double','char','double',...
'double','logical'};
Initialize and Configure FixedWidthImportOptions Object
Initialize a FixedWidthImportOptions object and configure its properties to match the properties of the data in fixed_width_patients_subset_perfect.txt.
opts = fixedWidthImportOptions('NumVariables',NumVariables,... 'DataLines',DataStartLine,... 'VariableNames',VariableNames,... 'VariableWidths',VariableWidths,... 'VariableTypes',DataType);
Import Table
Use readtable with the FixedWidthImportOptions object to import the table.
T = readtable(filename,opts)
T=10×7 table LastName Gender Age Location Height Weight Smoker ____________ ______ ___ _____________________________ ______ ______ ______
{'Smith' } Male 38 {'County General Hospital' } 71 176 true
{'Johnson' } Male 43 {'VA Hospital' } 69 163 false
{'Williams'} Female 38 {'St. Mary's Medical Center'} 64 131 false
{'Brown' } Female 49 {'County General Hospital' } 64 119 false
{'Miller' } Female 33 {'VA Hospital' } 64 142 true
{'Wilson' } Male 40 {'VA Hospital' } 68 180 false
{'Taylor' } Female 31 {'County General Hospital' } 66 132 false
{'Thomas' } Female 42 {'St. Mary's Medical Center'} 66 137 false
{'Jackson' } Male 25 {'VA Hospital' } 71 174 false
{'Clark' } Female 48 {'VA Hospital' } 65 133 false Import Messy Data from Fixed-Width Formatted Text File
Define an import options object to import messy data from a fixed-width formatted text file. Configure the object to handle the messy data and use it to import the table.
Load and Preview Fixed-Width Text File
Load the file fixed_width_patients_subset_messy.txt and preview its contents in a text editor. A screen shot is shown below. The screen shot shows that the file contains:
- Empty lines – Lines 7, 12, and 13
- An extra column – Column 8
- Missing data – Lines 1, 4, 9 and 11
- Partial fields – Last 3 rows
filename = 'fixed_width_patients_subset_messy.txt';
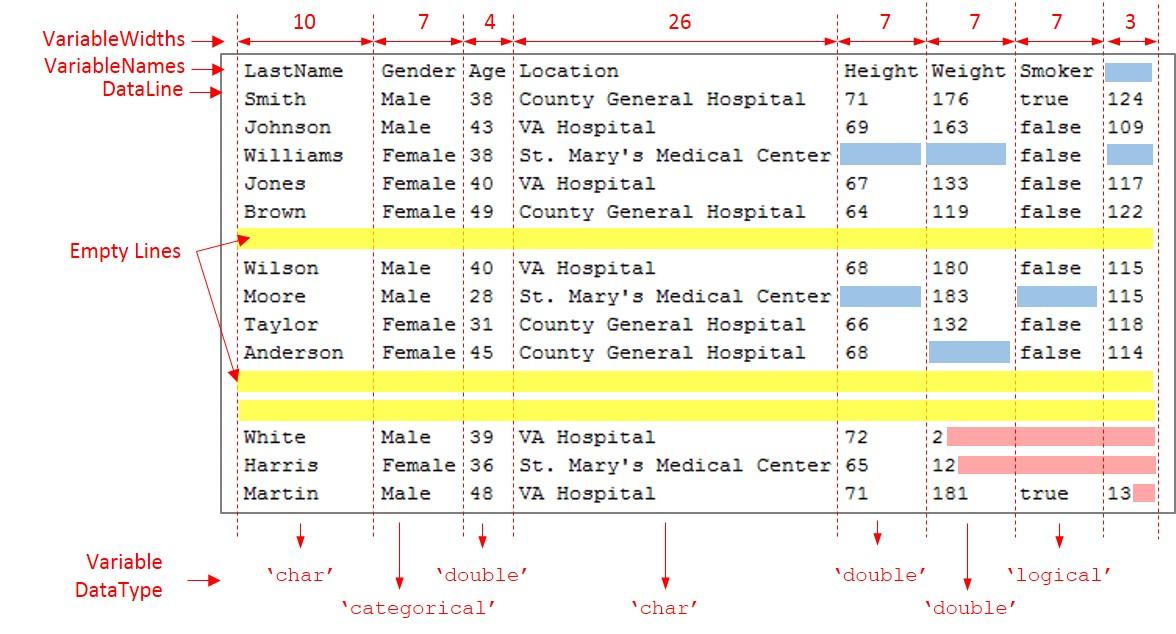
Examine and Capture Properties of Fixed-Width File
The fixed-width text file has tabular data organized by the starting location, number of variables, variable names, and variable widths. Capture these properties and the data type you want to use for the variables.
DataStartLine = 2;
NumVariables = 7;
VariableNames = {'LastName','Gender','Age','Location','Height',...
'Weight','Smoker'};
VariableWidths = [ 10, 7, 4, 26, 7, ...
7, 7 ] ;
DataType = {'char','categorical','double','char','double',...
'double','logical'};
Initialize FixedWidthImportOptions Object and Set Up Variable Properties
Initialize a FixedWidthImportOptions object and configure its properties to match the properties of the data.
opts = fixedWidthImportOptions('NumVariables',NumVariables,... 'DataLines',DataStartLine,... 'VariableNames',VariableNames,... 'VariableWidths',VariableWidths,... 'VariableTypes',DataType);
Set Up EmptyLinesRule, Missing Rule, and ExtraColumnsRule
Read the empty lines in the data by setting the EmptyLineRule to 'read'. Next, fill the missing instances with predefined values by setting the MissingRule to 'fill'. Finally, to ignore the extra column during the import, set the ExtraColumnsRule to 'ignore'. For more information on the properties and their values, see documentation for FixedWidthImportOptions.
opts.EmptyLineRule = 'read'; opts.MissingRule = 'fill'; opts.ExtraColumnsRule ='ignore';
Set Up PartialFieldRule
Partial fields occur when the importing function reaches the end-of-line character before the full variable width is traversed. For example, in this preview, the last three rows from the file fixed_width_patients_subset_messy.txt. Here, in the last row of the last column, the end-of-line character appears after two places from the start of the field, before the full variable-width of three is reached.

This occurrence of a partial field sometimes can indicate an error. Therefore, use the PartialFieldRule to decide how to handle this data. To keep the partial field data and convert it to the appropriate data type, set the PartialFieldRule to 'keep'. For more information on the PartialFieldRule, see documentation for FixedWidthImportOptions.
opts.PartialFieldRule = 'keep';
Import Table
Import the table by using readtable function and the FixedWidthImportOptions object and preview the data.
T = readtable(filename,opts)
T=15×7 table LastName Gender Age Location Height Weight Smoker ____________ ___________ ___ _____________________________ ______ ______ ______
{'Smith' } Male 38 {'County General Hospital' } 71 176 true
{'Johnson' } Male 43 {'VA Hospital' } 69 163 false
{'Williams'} Female 38 {'St. Mary's Medical Center'} NaN NaN false
{'Jones' } Female 40 {'VA Hospital' } 67 133 false
{'Brown' } Female 49 {'County General Hospital' } 64 119 false
{0×0 char } <undefined> NaN {0×0 char } NaN NaN false
{'Wilson' } Male 40 {'VA Hospital' } 68 180 false
{'Moore' } Male 28 {'St. Mary's Medical Center'} NaN 183 false
{'Taylor' } Female 31 {'County General Hospital' } 66 132 false
{'Anderson'} Female 45 {'County General Hospital' } 68 NaN false
{0×0 char } <undefined> NaN {0×0 char } NaN NaN false
{0×0 char } <undefined> NaN {0×0 char } NaN NaN false
{'White' } Male 39 {'VA Hospital' } 72 2 false
{'Harris' } Female 36 {'St. Mary's Medical Center'} 65 12 false
{'Martin' } Male 48 {'VA Hospital' } 71 181 true Version History
Introduced in R2016b
R2018b: Create options object using fixedWidthImportOptions function
Use the fixedWidthImportOptions function to create aFixedWidthImportOptions object. Previously, you could create this object only by using the detectImportOptions function.