Gases Solved in Water - Diffusion Coefficients (original) (raw)
Diffusion flux [kg/m2s] tells how fast a substanse solved in another substance flows due to concentration gradients. Diffusion constants [m2/s] for several gases in water.
Fick's first law states that a substance will flow from region with high concentration to a region of low concentration . Fick's law can be expressed as
J = -D dφ/dx (1)
where
J = diffusion flux - the amount of substance that flows through an unit area per unit time (mass or mol /(m2s))
D = diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
dφ = change in concentration of substance (mass or mol/m3)
dx = change in length (m)
For simple one-dimensional transport, the diffusion coefficient describes the time–rate of change of concentration . The diffusion coefficient varies from substance to substance and with temperature.
See Water and Heavy Water - thermodynamic properties.
See also Water Boiling points at high pressure, Boiling points at vacuum pressure, Density, specific weight and thermal expansion coefficient, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity, Enthalpy and entropy, Heat of vaporization, Ionization Constant, pKw , of normal and heavy water, Melting points at high pressure, Saturation pressure, Specific gravity, Specific heat (heat capacity) and Specific volume for online calculatores, and similar figures and tables as shown below, as well as Air - Diffusion Coefficients of Gases in Excess of Air
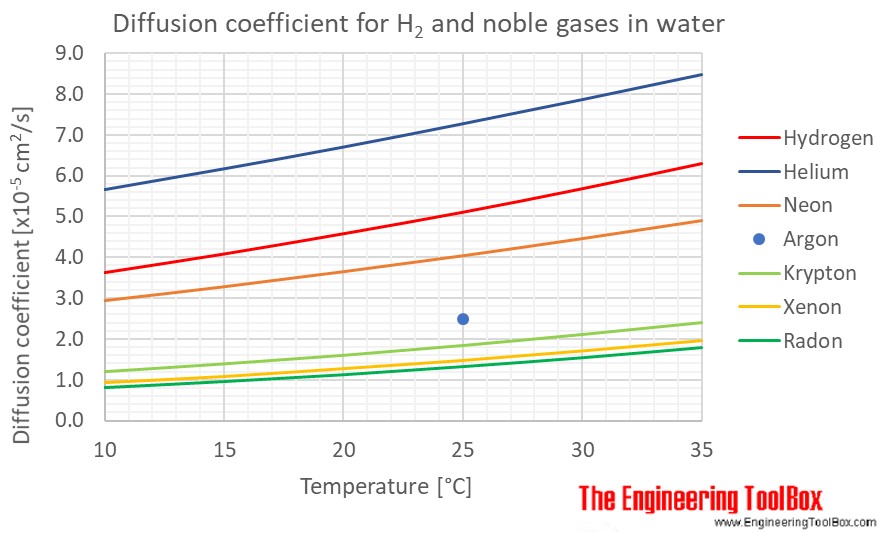
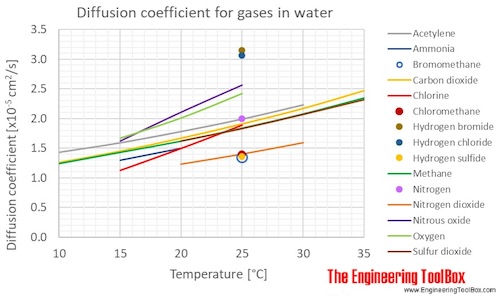
Diffusion coefficients for some common gases in water:
(Gas–liquid diffusion coefficients are difficult to measure, and since the values below are from different sources and different measuring methods, there is some uncertainty about the values)
Gases Solved in Water - Diffusion Coefficients
| Gas in water | Diffusion coefficient, D, (×10-5cm2/s ) at atmospheric pressure and given temperatures | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 °C | 15 °C | 20 °C | 25 °C | 30 °C | 35 °C | ||
| Name | Formula | 50 °F | 59 °F | 68 °F | 77 °F | 86 °F | 95 °F |
| Acetylene | C2H2 | 1.43 | 1.59 | 1.78 | 1.99 | 2.23 | |
| Ammonia | NH3 | 1.30 | 1.50 | ||||
| Argon | Ar | 2.50 | |||||
| Bromomethane | CH3Br | 1.35 | |||||
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | 1.26 | 1.45 | 1.67 | 1.91 | 2.17 | 2.47 |
| Chlorine | Cl2 | 1.13 | 1.50 | 1.89 | |||
| Chloromethane | CH3Cl | 1.40 | |||||
| Dichlorofluorumethane | CHCl2F | 1.80 | |||||
| Helium | He | 5.67 | 6.18 | 6.71 | 7.28 | 7.87 | 8.48 |
| Hydrogen | H2 | 3.62 | 4.08 | 4.58 | 5.11 | 5.69 | 6.31 |
| Hydrogen bromide | HBr | 3.15 | |||||
| Hydrogen chloride | HCl | 3.07 | |||||
| Hydrogen sulfide | H2S | 1.36 | |||||
| Krypton | Kr | 1.20 | 1.39 | 1.60 | 1.84 | 2.11 | 2.40 |
| Methane | CH4 | 1.24 | 1.43 | 1.62 | 1.84 | 2.08 | 2.35 |
| Neon | Ne | 2.93 | 3.27 | 3.64 | 4.03 | 4.45 | 4.89 |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 2.00 | |||||
| Nitrogen dioxide | NO2 | 1.23 | 1.40 | 1.59 | |||
| Nitrous oxide | N2O | 1.62 | 2.11 | 2.57 | |||
| Oxygen | O2 | 1.67 | 2.01 | 2.42 | |||
| Radon | Rn | 0.81 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 1.33 | 1.55 | 1.80 |
| Sulfur dioxide | SO2 | 1.62 | 1.83 | 2.07 | 2.32 | ||
| Xenon | Xe | 0.93 | 1.08 | 1.27 | 1.47 | 1.70 | 1.95 |
My Short List
Related Topics
Properties of gases, fluids and solids. Densities, specific heats, viscosities and more.
Design of steam & condensate systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines, system configuration and more.
Calculate heat, work, temperature and energy. The thermodynamics of steam and condensate systems. Water and Ice properties.
Work, heat and energy systems.
Design of hot and cold water service and utility systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines and more.
Related Documents
Heavy Water - Thermophysical Properties
Thermodynamic properties of heavy water (D2O) like density, melting temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of fusion, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more.
Ice and Water - Melting Points vs. Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables with melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia (0 to 2000 bara). Temperature given as °C, °F, K and °R.
Pollution Concentration in Rooms
Concentration of a pollution in a limited space as a room depends on the amount of polluted material spread in the room, supply of fresh air, outlets positions and construction, principles used for supply and outlet from the space.
Solubility of Gases in Water vs. Temperature
Solubility of Ammonia, Argon, Carbon Dioxide, Carbon Monoxide, Chlorine, Ethane, Ethylene, Helium, Hydrogen, Hydrogen Sulfide, Methane, Nitrogen, Oxygen and Sulfur Dioxide in water.
Water - Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions
Figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, Prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy).
Water - Specific Gravity vs. Temperature
Figures and tables showing specific gravity of liquid water in the range of 32 to 700 °F or 0 to 370°C, using water density at four different temperatures as reference.


