Eccrine syringofibroadenoma (original) (raw)
Skin nonmelanocytic tumor
Adnexal tumors
Sweat gland derived (apocrine & eccrine glands)
Eccrine syringofibroadenoma
Last author update: 6 February 2024
Last staff update: 6 February 2024
Copyright: 2002-2024, PathologyOutlines.com, Inc.
PubMed Search: Eccrine syringofibroadenoma
Cite this page: Ghaoui N, Brem CE. Eccrine syringofibroadenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticacrosyringealadenomatosis.html. Accessed December 29th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign eccrine proliferation of anastomosing cords with ductal structures set in a fibrovascular stroma, often located on the extremities
Essential features
- Erythematous, solitary or multiple papules and nodules often on acral sites
- Association with Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome and Clouston syndrome
- Thin anastomosing cords and strands of basaloid monomorphous cuboidal cells extending from the basal layer of epidermis into dermis with ductal structures and set in a fibrovascular stroma
Terminology
- Eccrine syringofibroadenoma (of Mascaro)
- Other names include
- Eccrine syringofibroadenomatous hyperplasia
- Acrosyringeal adenomatosis
- Eccrine poromatosis
- Linear eccrine poroma
- Acrosyringeal nevus or acrosyringeal nevus of Weedon and Lewis
- Nevus syringoadenomatosus papilliferum
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare
- Wide age range, most cases presenting in the seventh to eighth decade (Am J Dermatopathol 1992;14:328)
- Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome associated cases usually present in adolescence; slightly later presentation in Clouston syndrome
- No clear racial or gender predilection
Sites
- Predilection for extremities, especially acral sites
- Several nonacral sites, such as eyelid, perianal region and scalp, reported (Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 2013;13:328, Indian J Dermatol 2017;62:548, J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2022;15:335)
Pathophysiology
- Morphologic, immunohistochemical and electron microscopic evidence supports origin from eccrine duct cells
- Reactive subtype postulated to be induced by repair / remodeling process (An Bras Dermatol 2021;96:255)
Etiology
- Unclear; neoplastic / tumoral, hamartomatous and reactive origins postulated
- Presence in ectodermal dysplasia supports a tumoral or hamartomatous process (J Dermatol 2022;49:e451)
- Rare cases with malignant transformation support a neoplastic process (Am J Dermatopathol 2020;42:780)
- Cases with associated inflammatory dermatoses and benign or malignant epithelial neoplasms support a reactive process (An Bras Dermatol 2021;96:255)
Clinical features
- Presents as slow growing, solitary or multiple, flesh colored nodule(s)
- 5 major clinical types (J Am Acad Dermatol 1997;36:569)
- Solitary: most common form, often on lower extremities
- Multiple with hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome and Clouston syndrome): palms and soles, younger patients (15 - 25 years old)
- Multiple without associated cutaneous findings: palms and soles
- Nevoid (i.e., nonfamilial unilateral linear eccrine syringofibroadenoma [ESFA]): rare, unilateral linear papules and plaques
- Reactive, as can be seen in association with the following
* Inflammatory dermatoses / processes (i.e., erosive lichen planus, uncontrolled psoriasis, bullous pemphigoid, epidermolysis bullosa, primary cutaneous amyloidosis, thermal scar, venous stasis, chronic diabetic foot ulcer, neuropathy, peristomal skin)
* Infectious etiologies (i.e., leprosy, HPV)
* Neoplasms / tumors (i.e., nevus sebaceus, clear cell acanthoma, acantholytic dyskeratotic acanthoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma and Merkel cell carcinoma)
- Associated syndromes
- Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome (OMIM: Schopf-Schulz-Passarge Syndrome; SSPS [Accessed 11 October 2023])
* Autosomal recessive disorder due to a homozygous mutation of the WNT10A gene (chromosome 2q35)
* Clinical features include palmoplantar keratoderma, hypodontia, hypotrichosis, hyperhidrosis, eyelid hidrocystomas, nail dystrophy and eccrine syringofibroadenoma (Br J Dermatol 2014;171:1211, J Cutan Pathol 2020;47:987) - Clouston syndrome (OMIM: Clouston Syndrome [Accessed 11 October 2023])
* Autosomal dominant disorder due to heterozygous mutations in the gap junction beta 6 (GJB6) gene (chromosome 13q12.11) that encodes gap junction protein beta 6 (i.e., connexin 30) (Front Med 2023;17:330)
* Clinical features include palmoplantar keratoderma, alopecia, nail dystrophy and eccrine syringofibroadenoma (Int J Dermatol 2019;58:e143)
- Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome (OMIM: Schopf-Schulz-Passarge Syndrome; SSPS [Accessed 11 October 2023])
Diagnosis
- Biopsy / histologic examination and clinicopathologic correlation necessary for diagnosis
Prognostic factors
- Benign lesion(s)
- 1 case of reactive ESFA with spontaneous involution (Clin Exp Dermatol 2009;34:e66)
- Rare malignant transformation in longstanding lesions (Am J Dermatopathol 2020;42:780)
Case reports
- 31 year old man with perianal ESFA following deep bacterial infection (Indian J Dermatol 2017;62:548)
- 36 year old woman with palmar syringofibroadenoma-like lesions in the setting of Clouston syndrome treated with CO2 ablative laser (JAAD Case Rep 2023:39:61)
- 72 year old woman with reactive ESFA in association with a Merkel cell carcinoma excision scar (Am J Dermatopathol 2023;45:137)
- 77 year old man with ESFA associated with basal cell carcinoma (Dermatol Surg 2018;44:738)
- 97 year old woman with acantholytic dyskeratotic acanthoma accompanying syringofibroadenomatous hyperplasia (J Cutan Pathol 2021;48:451)
Treatment
- Single lesions treated by surgical excision or cryotherapy (J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2016;106:237)
- Therapy for cases with multiple lesions depends on size and location
- Laser therapy with dual pulse width flashlamp (Dermatol Surg 1999;25:418)
- Etretinate oral therapy in diffuse lesions (J Dermatol 1999;26:36)
- CO2 laser (JAAD Case Rep 2023:39:61)
- Radiotherapy (Dermatol Ther 2010:23:S20)
- Topical corticosteroids (An Bras Dermatol 2021;96:255)
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
Vegetating erythematous plaque
Skin colored fibrotic nodule
Pink nodules and plaques
Coalescing palmar papules
Multiple irregular nodules
Fleshy nodules of ESFA
Gross description
- Verrucous erythematous papules, nodules and ulcerative plaques
- Multiple nodules may be arranged in a symmetrical or unilateral nevoid fashion
Microscopic (histologic) description
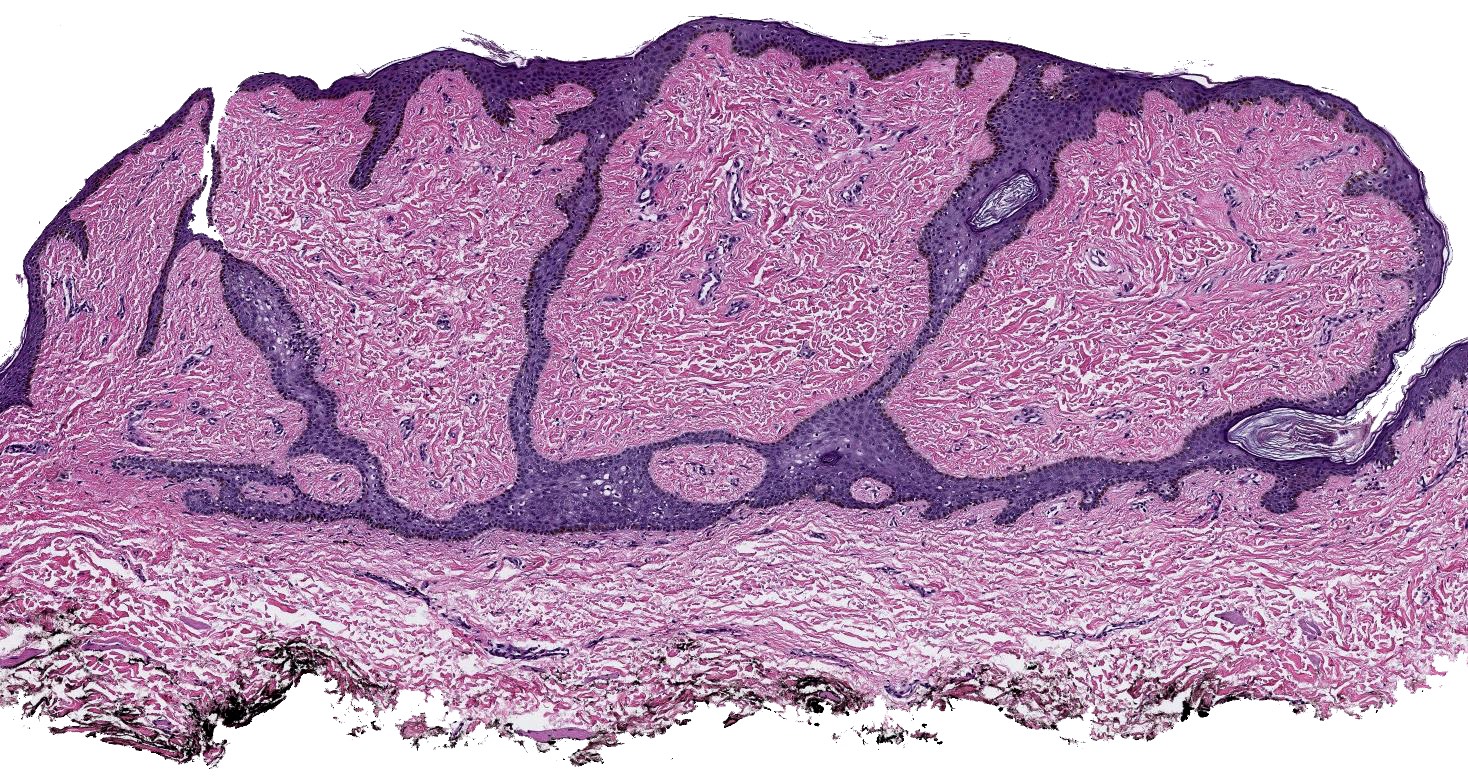
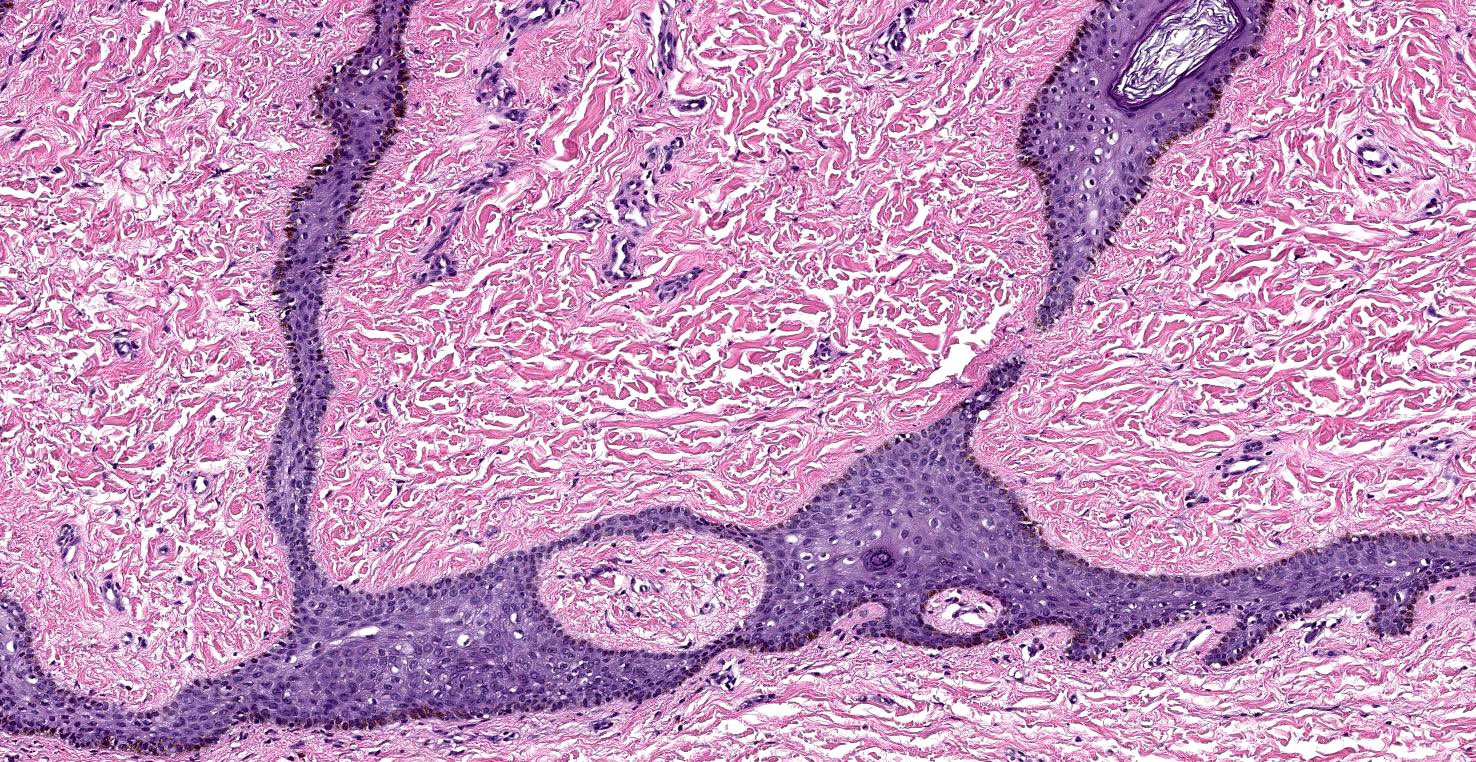
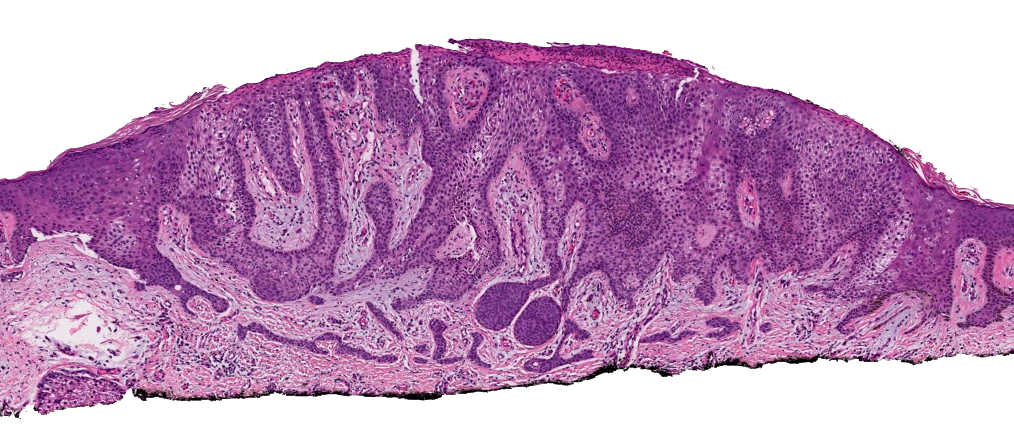
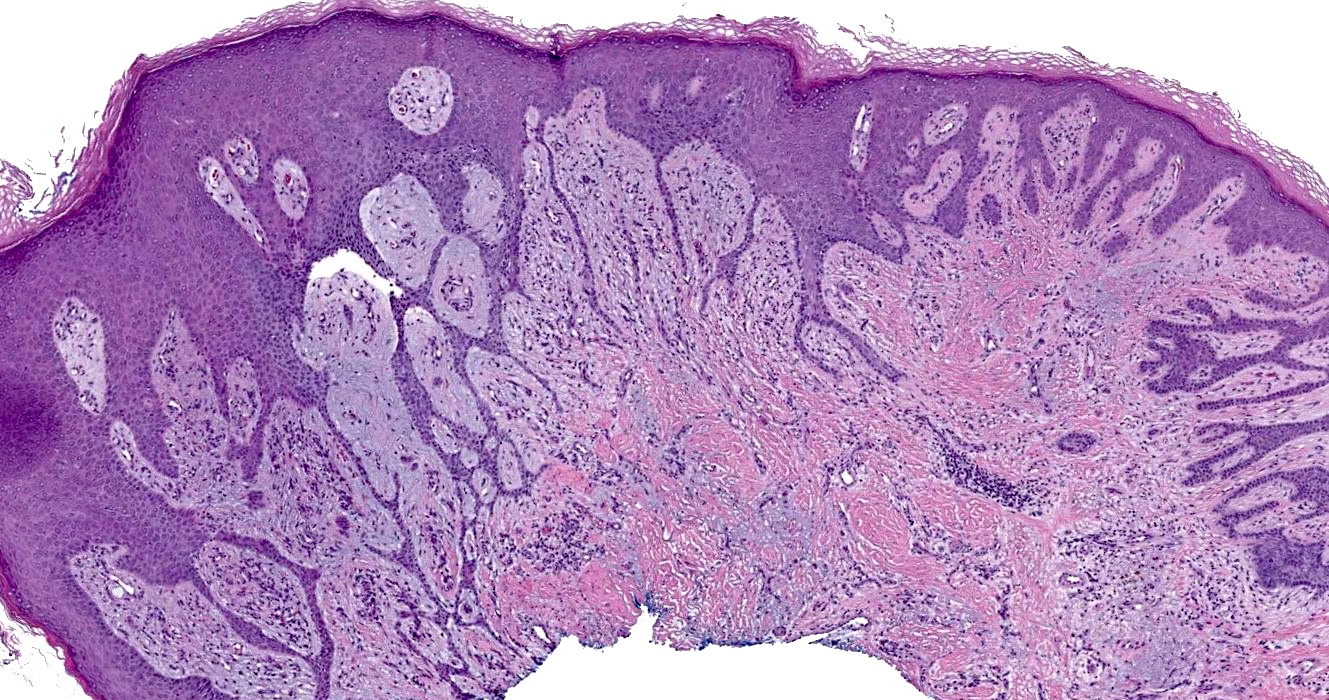
- Proliferation of thin anastomosing reticulated epithelial cords and strands often forming a lattice and extending from the epidermis into the dermis (J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2022;15:335)
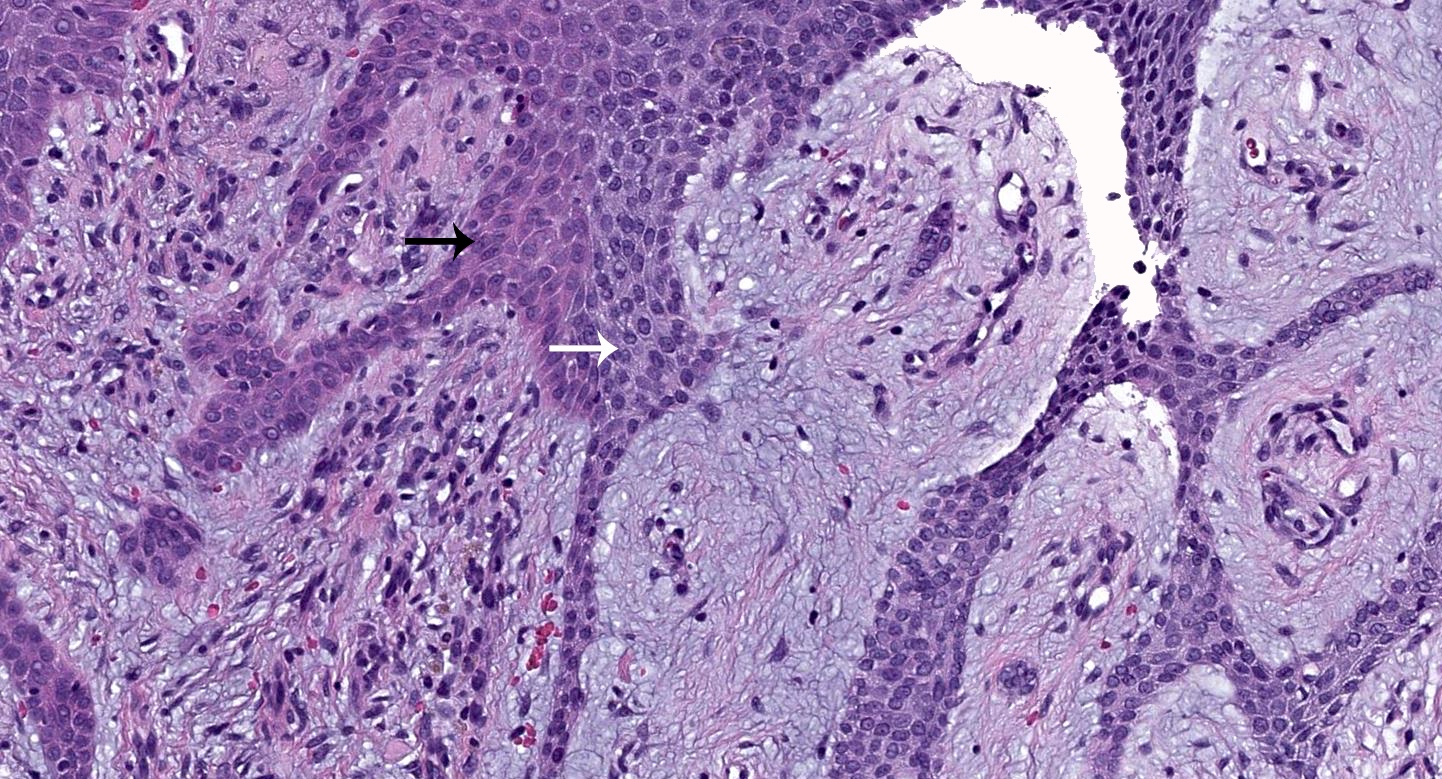
- Lesional cells are monomorphous, basaloid, cuboidal and slightly smaller than adjacent keratinocytes
- Epithelial cords contain structures resembling eccrine ducts (Ann Dermatol 2020;32:57)
- Background fibrovascular stroma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Candice E. Brem, M.D.
Circumscribed papulonodular lesion
Background fibrous stroma
CCA with ESFA
Ductal structures
Epidermal based interconnected strands
Lattice-like architecture
Basaloid cuboidal lesional cells
Positive stains
- Periductal / ductal structures: CEA, EMA, involucrin, filaggrin, CK6, CK8, CK10, CK18, CK19 (Am J Dermatopathol 1996;18:207, Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:171)
- Strands and sheets of cells: CK6, AE1, MNF116, AE3, CK 34 beta E12 (Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:171, J Cutan Pathol 2000;27:164)
Electron microscopy description
- Tumor cells with tonofilaments / desmosomes, numerous glycogen granules
- Basal lamina
- Globular keratohyalin granules around ducts / cysts
- No lamellar granules
- Poorly developed cornified cell envelopes (Am J Dermatopathol 1996;18:207)
Videos
Eccrine syringofibroadenoma: rare skin adnexal tumor / pattern
Sample pathology report
- Leg, shave biopsy:
- Benign appendageal neoplasm with eccrine differentiation consistent with an eccrine syringofibroadenoma (see comment)
- Comment: The lesion extends to the deep margin. The specimen exhibits an epidermal based proliferation of monomorphous basaloid cells arranged as anastomosing cords forming a lattice with intermixed ductal structures and set in a fibrovascular stroma. These findings support the histologic diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Fibroepithelioma of Pinkus:
- Buds of basaloid epithelium characteristic for basal cell carcinoma
- No duct formation noted within the anastomosing epithelial cords
- Poroma and hidroacanthoma simplex:
- Shares eccrine histogenesis
- Lacks the reticular and corded architecture of ESFA
- Porocarcinoma:
- Lacks corded architecture
- Has malignant cytologic changes
- Tumor of the follicular infundibulum:
- Shares anastomosing strands but forms a plate-like structure in the dermis and lacks ductal structures
- Squamous cell carcinoma with ductal differentiation:
- Infiltrative pattern with cytologic atypia
Board review style question #1
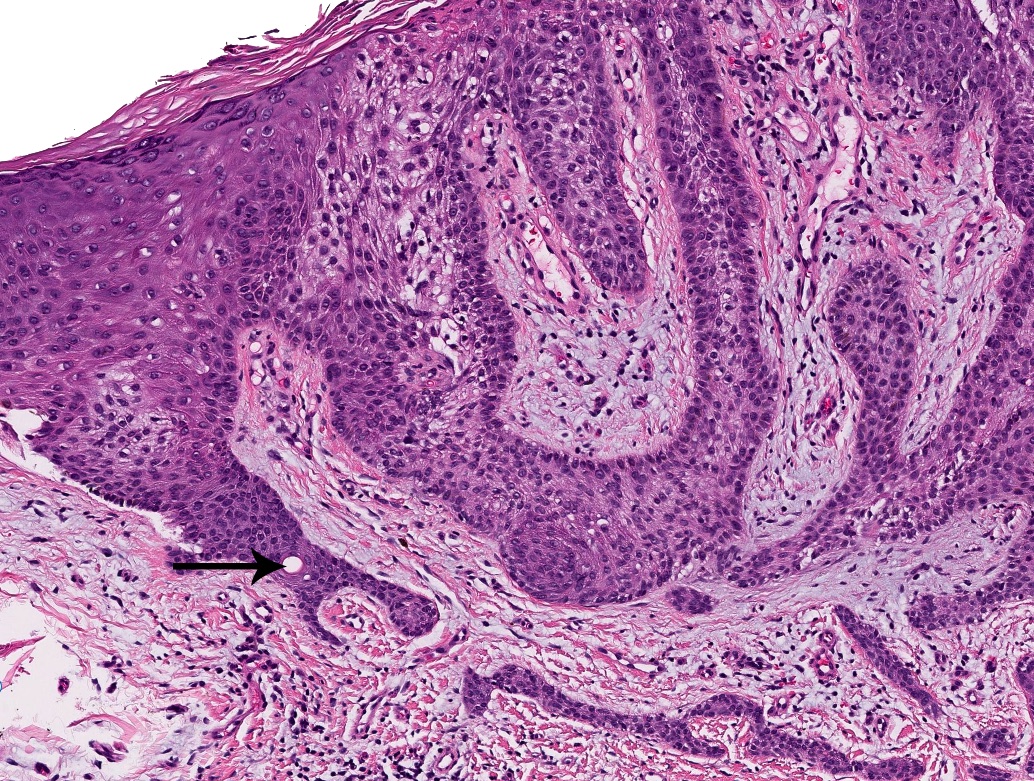
A 74 year old woman presents with a 1 year history of asymptomatic, erythematous papules on the left heel. A subsequent shave biopsy is performed (see image above). Few intermixed ducts in the epithelial cords are also noted on examination of multiple tissue levels. What is the best histologic diagnosis for this lesion?
- Basal cell carcinoma, infiltrative type
- Eccrine syringofibroadenoma
- Porocarcinoma
- Poroma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
B. Eccrine syringofibroadenoma (ESFA). The clinical presentation paired with the histologic features of anastomosing reticulated cords and strands of basaloid monomorphous cuboidal cells extending from the epidermis into dermis with few ductal structures set in a fibrovascular stroma are consistent with eccrine syringofibroadenoma. Answer A is incorrect because basal cell carcinoma demonstrates peripheral palisading, clefting and a fibromucinous stroma, while generally lacking intermixed ductal structures. Answer D is incorrect because poroma lacks the reticular and corded architecture of ESFA. Answer C is incorrect because porocarcinoma lacks the corded architecture and has malignant cytologic changes. Answer E is incorrect because squamous cell carcinomas often demonstrate eosinophilic to glassy keratinocytes, cytologic atypia and an infiltrative growth pattern.
Reference: Eccrine syringofibroadenoma
Board review style question #2
In the pediatric population, eccrine syringofibroadenoma (ESFA) has been associated with which genetic disorder?
- Birt-Hogg-Dubé
- Brooke-Spiegler
- Rubinstein-Taybi
- Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge
Board review style answer #2
D. Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge. ESFA has been recognized as a cutaneous marker of Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome. Answer C is incorrect because to date, no cases of ESFA have been seen in Rubinstein-Taybi, a syndrome usually associated with pilomatricomas, hemangiomas and keloids. Answer A is incorrect because Birt-Hogg-Dubé patients have a high frequency of developing fibrofolliculomas, trichodiscomas and lipomas. Answer B is incorrect because Brooke-Spiegler, due to a CYLD mutation, has an increased risk of developing spiradenomas, cylindromas, trichoepitheliomas and basal cell carcinomas.
Reference: Eccrine syringofibroadenoma