The exosome contains domains with specific endoribonuclease, exoribonuclease and cytoplasmic mRNA decay activities (original) (raw)
- Article
- Published: 07 December 2008
- Borislava Tsanova1,
- Ana Barbas2,
- Filipa Pereira Reis2,
- Eeshita Ghosh Dastidar1,
- Maya Sanchez-Rotunno1,
- Cecília Maria Arraiano2 &
- …
- Ambro van Hoof1
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology volume 16, pages 56–62 (2009)Cite this article
- 2265 Accesses
- 268 Citations
- 4 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
The eukaryotic exosome is a ten-subunit 3′ exoribonucleolytic complex responsible for many RNA-processing and RNA-degradation reactions. How the exosome accomplishes this is unknown. Rrp44 (also known as Dis3), a member of the RNase II family of enzymes, is the catalytic subunit of the exosome. We show that the PIN domain of Rrp44 has endoribonucleolytic activity. The PIN domain is preferentially active toward RNA with a 5′ phosphate, suggesting coordination of 5′ and 3′ processing. We also show that the endonuclease activity is important in vivo. Furthermore, the essential exosome subunit Csl4 does not contain any domains that are required for viability, but its zinc-ribbon domain is required for exosome-mediated mRNA decay. These results suggest that specific exosome domains contribute to specific functions, and that different RNAs probably interact with the exosome differently. The combination of an endoRNase and an exoRNase activity seems to be a widespread feature of RNA-degrading machines.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Virtually all RNAs are processed from longer precursors. Although the removal of 3′ extensions seems to be a simple enzymatic reaction, eukaryotic cells contain multiple endoribonucleases (endoRNases) and 3′ exoribonucleases (exoRNases)1,2,3,4. These exoRNases can act redundantly for some reactions, but are specific for other functions5. In addition to these RNA-processing reactions that generate mature RNAs, 3′ exoRNases and endonucleases also carry out mRNA-degradation reactions6,7 that can be an important determinant for mRNA quality control8,9. The same RNase can process some substrates and completely degrade others. It is largely unknown what determines the specificity of different RNases for their particular substrates, or for processing versus decay.
The exosome is a major 3′ exoRNase that is present in all eukaryotes, but whose function has been most extensively characterized in Saccharomyces cerevisiae10,11. The yeast exosome is responsible for the 3′-end processing of stable RNAs including ribosomal RNA (rRNA), small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), as well as the degradation of RNAs such as the 5′ external transcribed spacer (ETS) of the rRNA precursor and aberrant mRNAs that lack a stop codon or a poly(A) tail7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14.
The core exosome contains nine subunits and shows extensive structural similarity to bacterial PNPase and archaeal exosomes15,16,17,18,19,20 (Fig. 1a, above). These nine subunits are all essential for viability. Six subunits have an RNase PH domain and form a ring structure in the exosome15. Although these six subunits show clear sequence and structural similarity to RNases, all six subunits in the yeast and human exosome lack important catalytic residues and are inactive15,21. The six PH-ring subunits cannot assemble into a PH-ring in vitro, but, when the three cap proteins are added, a stable core exosome can be assembled15. The crystal structure shows that each cap protein contacts two neighboring subunits of the PH ring. These observations suggest that the cap proteins carry out an essential structural role by bridging interactions between PH domains15 (Fig. 1a, above). A second possible function of the cap proteins is to bind exosome substrates, as each contains three putative RNA binding domains11,20,22. Finally, a point mutation in one of the cap proteins (Csl4) disrupts the interaction between the core exosome and one of its cofactors8. The exosome requires many cofactors, and a third possible function for the cap proteins is to provide binding sites for these cofactors.
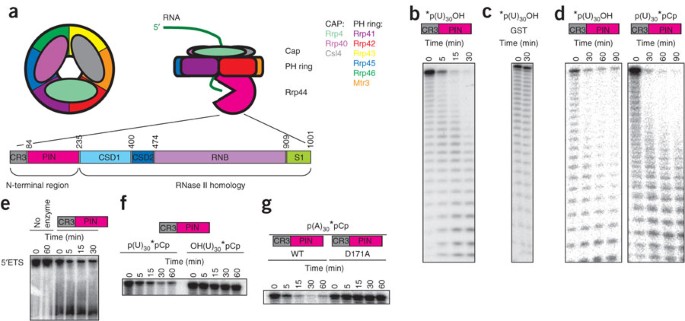
Figure 1: The N-terminal region of Rrp44 has RNase activity.
(a) The yeast exosome contains three layers. The exosome contains a PH ring of six proteins with an RNase PH domain. Assembly and/or stability of the PH ring requires three additional proteins that form a cap on one side of the ring. The exoRNase activity of the exosome is provided by a tenth subunit (Rrp44) that associates with the bottom of the ring. RNA substrates are thought to associate with the cap proteins and pass through the central channel in the PH ring, being degraded by Rrp44 after they emerge from the bottom of the ring. Below is a schematic representation of Rrp44's domains. (b) The N-terminal region of Rrp44, which contains a CR3 domain and a PIN domain, has RNase activity in vitro. The N-terminal part of Rrp44 was purified as a GST-fusion recombinant protein from E. coli and incubated with 5′ end–labeled U30 RNA. (c) GST by itself, purified and incubated under identical conditions, does not have RNase activity. (d) The N-terminal region of Rrp44 degrades both 5′ end–labeled and 3′ end–labeled substrates to smaller labeled oligoribonucleotides, suggesting that this region acts as an endonuclease. (e) The N-terminal region of Rrp44 degrades an internally labeled RNA corresponding to the 5′ ETS in vitro. (f) The N-terminal region of Rrp44 prefers substrates with a 5′ phosphate (left) over those with a 5′ hydroxyl group (right). The apparent slight change in mobility in the right-hand gel is an artifact of this particular gel and does not reflect a slow degradation of the 5′ hydroxyl substrate. (g) Mutation of the conserved acidic amino acid residue Asp171 to alanine in the N-terminal region of Rrp44 abolishes RNase activity. The asterisks in b–d and f,g indicate the position of the P32 label.
Although the nine subunit exosome core shows remarkable structural similarity to the bacterial PNPase and the archaeal exosome, the yeast exosome contains a tenth essential subunit (Rrp44), which is homologous to bacterial RNase II (Fig. 1a) and is responsible for the 3′ exoRNase activity of the exosome21,23,24,25,26,27. Notably, although Rrp44 is an essential gene, a point mutation that inactivates its exoRNase activity in vitro is viable21, suggesting that either the exoRNase activity may not be a central feature of the exosome or the point-mutant protein retains partial exoribonucleolytic activity in vivo.
The N terminus of Rrp44 contains a CR3 domain and a PIN domain (Fig. 1a, below). The CR3 domain is a small domain of unknown function that contains three conserved cysteine residues. PIN domains were initially thought to have some regulatory or signaling function, but recent crystal structures of PIN domains revealed a putative active site with similarity to RNase H28,29. Indeed, some PIN domains have endoRNase activity, including the SMG6 protein, which is involved in nonsense-mediated decay28,29,30,31,32,33. PIN domains contain four acidic amino acid residues (Asp91, Glu120, Asp171 and Asp198 in Rrp44), and mutations in the third residue abolish the activity of PIN domains in vitro and in vivo30,34,35.
In this paper, we show that the Rrp44 PIN domain is an active endoRNase, revealing that the exosome has endoRNase activity in addition to its known exoRNase activity. Furthermore, we characterize the functions of the cap proteins of the yeast exosome and show that, whereas Rrp4 and Rrp40 might have a largely structural role, Csl4 does not seem to have an important role in exosome structure but, instead, seems to have specific domains that are required for specific functions.
Results
The exosome contains an endoRNase domain
To test whether the Rrp44 PIN domain contains endonuclease activity, we purified a truncated Rrp44 as a glutathione _S_-transferase (GST) fusion from Escherichia coli. This truncated Rrp44 contains the PIN domain, but lacks the RNB domain, and has robust nuclease activity in vitro on several RNA substrates (Fig. 1), whereas GST by itself does not (Fig. 1c). The activity level of the truncated Rrp44 was similar to the activity level of the full-length protein (although under different conditions; Supplementary Fig. 1 online). Mutation of the third conserved acidic residue (Asp171) in the Rrp44 PIN domain abolished the endoRNase activity (Fig. 1g), as has been shown for some other PIN domains either in vitro or in vivo30,34,35. We conclude that the PIN domain of Rrp44 is a nuclease.
Other PIN domains and the related RNases H act as endonucleases. To test whether the Rrp44 PIN acts as an endonuclease we used 5′- or 3′-labeled substrates. An exonuclease will yield only labeled mononucleotides with one of these substrates. In contrast, the PIN domain yielded a similar pattern of labeled oligonucleotides with each substrate, showing that this domain acts as an endonuclease (Fig. 1d). Notably, the PIN domain was dramatically more active on substrates with a 5′ monophosphate than on substrates with a 5′ hydroxyl group (Fig. 1f), which may have important implications (see Discussion). As expected for an endonuclease, the PIN domain also had some activity on circular U30 (Supplementary Fig. 1b). However, degradation of circular RNA was inefficient, probably because it lacks a free 5′ phosphate. All of these results indicate that the Rrp44 PIN domain is an active endoRNase, as has been shown for SMG6 (refs. 29,32).
Either RNase activity can form an active exosome
To address whether this endonuclease activity is important for exosome function, we generated truncations and point mutants of Rrp44. C-terminal truncations that removed the RNase II homology, but left the CR3 and PIN domains, allowed for slow growth (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Fig. 2 online). Previously it was shown that a point mutation inactivating the catalytic activity of the RNB domain is viable21,36. The residual growth we observed upon deletion of the RNB domain rules out the possibility that the mutated RNB domain was viable owing to some low-level activity in vivo. Instead, our results show that exoRNase activity is not a crucial feature of the exosome core. C-terminal truncations that also removed part of the PIN domain, or truncation of the N terminus, did not support any growth. The smallest viable Rrp44 allele we generated included the CR3 and PIN nuclease domains (amino acids 1–235). We conclude that the PIN domain is essential for exosome function, but we cannot exclude the alternative that the PIN domain (also) has functions separate from the exosome.
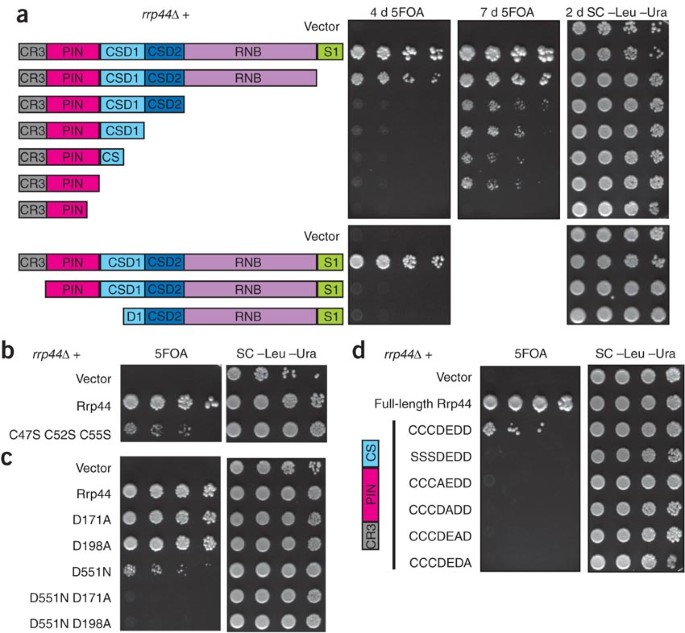
Figure 2: The PIN active site is important for exosome function.
(a) The N-terminal region of Rrp44 is required and sufficient for viability. An _rrp44_Δ strain complemented by full-length RRP44 on a plasmid with a URA3 marker was transformed with LEU2 plasmids encoding each of the depicted truncations. Growth on 5-fluoroorotic acid (5FOA) indicates that truncated Rrp44 can carry out the essential function of the exosome. The smallest complementing Rrp44 allele includes amino acids 1–235. Similar results were obtained with a GAL::rrp44 strain (Supplementary Fig. 2). (b) Mutation to serine of the three conserved cysteine residues in the CR3 domain reduces growth. (c) Mutations in the PIN domain active site residues of Rrp44 do not have a large effect on growth, but they are lethal in combination with a mutation of the active-site residue of the RNB domain. Similar results were obtained for the D91A and E120A mutations (Supplementary Fig. 3). (d) Mutations of the PIN domain active-site residues are lethal in combination with a truncation that removes the RNB domain. CCDEDD indicates Cys47, Cys52, Cys55, Asp91, Glu120, Asp171 and Asp198, which where mutated in the last five rows as indicated. SC –Leu –Ura is synthetic complete media lacking leucine and uracil included as a control.
To further address the importance of the CR3 and PIN domains, we made point mutants in conserved residues. Mutating the three conserved cysteines of the CR3 domain caused slow growth (Fig. 2b); thus, both N-terminal truncations and point mutants indicate an important role for the CR3 domain. In contrast, the D171A point mutation, which inactivates the PIN domain (or mutations in the other three conserved acidic residues), does not have an obvious growth phenotype (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Fig. 3 online). However, combining the viable PIN mutations with either the viable D551N or a viable C-terminal truncation resulted in no growth (Fig. 2c,d and Supplementary Fig. 3). These results suggest that either active site is sufficient for viability, but simultaneous inactivation of both catalytic sites results in a nonfunctional exosome.
The exosome carries out both RNA-processing and RNA-degradation reactions. Endonuclease activity might be well suited for processing reactions, but exonuclease activity would be more appropriate for degradation reactions. We therefore tested the hypothesis that the PIN domain of Rrp44 is sufficient for exosome-mediated RNA-processing reactions, whereas the RNB domain is required for exosome-mediated RNA decay. Truncations lacking the RNase II homologous domain cause the 5′ ETS and the 7S precursor of the 5.8S rRNA to accumulate (Fig. 3a). Similarly, 7S-processing and 5′ ETS–degradation intermediates accumulated as a result of the D551N mutation in the RNB domain. We did not observe any similar degradation or processing intermediates resulting from the D171A mutation in the PIN domain, and the effect of the combination of D551N with D171A seemed similar to that of the D551N single mutant (Fig. 3b). Thus, both degradation and processing functions of the exosome require the RNB domain. An alternative explanation for the presence of two catalytic sites is that the efficiency of the overall reaction is increased. Under this hypothesis, the endo- and exonuclease domains do not have separate substrates, but both may act together on most or all exosome substrates.
Figure 3: The RNB domain of Rrp44 is required for both RNA-processing and RNA-degradation activities of the exosome.
(a) The indicated Rrp44 truncations were expressed in a GAL::rrp44 yeast strain. RNA was isolated from cultures grown in dextrose (to inhibit expression of the GAL::rrp44 gene) and analyzed by northern blotting with probes that hybridize to the 7S precursor of 5.8S rRNA (above), the 5′ ETS of the rRNA (middle) and the RNA subunit of the signal recognition particle (SRP; below). The relative levels of the 7S pre-rRNA and the 5′ ETS were normalized for loading using the SRP signal and are indicated under the above and middle blots. Shown is a representative experiment. (b) RRP44 alleles containing the D171A mutation, the D551N mutation or the D171A D551N double mutation were introduced into a GAL::rrp44 yeast strain. Cultures were first grown in media containing galactose and then incubated in media containing glucose for the indicated time (in hours) and analyzed by northern blotting with probes that hybridize to the 5.8S rRNA (above), the 5′ ETS of the rRNA (middle) and the RNA subunit of the signal recognition particle (below). Shown is a representative experiment.
The essential Csl4 does not contain an essential domain
To gain further insight into the structure-function relationship of the exosome, we next focused on the function of the three cap proteins. The Csl4 subunit contains an N-terminal domain that resembles RPL27, a central S1 domain and a C-terminal domain that shows structural similarity to zinc ribbons, although the zinc-coordinating residues have been mutated. In addition, the yeast Csl4 contains a 38-residue linker that is absent in Csl4 from humans and most other eukaryotes. The first 22 residues of this inserted sequence include ten glutamate and two aspartate residues. To test which domains of Csl4 are essential, we made several truncations. Markedly, each of the domains could be removed, and either the RPL27-like or S1 plus zinc-ribbon domains are sufficient for the essential function of the exosome (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Fig. 4 online). Thus, the essential Csl4 subunit does not seem to have an essential domain.
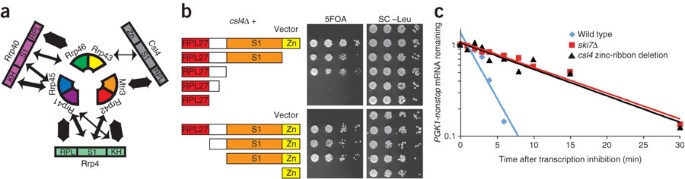
Figure 4: The essential Csl4 does not contain any essential domains, but its zinc-ribbon domain is required for cytoplasmic exosome-mediated mRNA decay.
(a) Rrp4 and Rrp40 make extensive contacts with two neighboring subunits of the PH ring. Csl4 makes extensive contacts with Mtr3 but relatively small contacts with Rrp43. The width of the double-headed arrows is proportional to the extent of the buried surface calculated using PyMol (http://pymol.sourceforge.net). (b) The essential Csl4 does not contain any essential domains. Csl4 contains a RPL27-like domain (red), a 38-residue linker not present in other eukaryotes (white), an S1 domain (orange) and a zinc ribbon–like domain that is missing the zinc-coordinating residues (yellow). A _csl4_Δ strain complemented by full-length CSL4 on a plasmid with a URA3 marker was transformed with LEU2 plasmids encoding the depicted truncations. Growth on 5-fluoroorotic acid (5FOA) indicates that truncated Csl4 can carry out the essential function of the exosome. Similar results were obtained with a GAL::csl4 strain (Supplementary Fig. 4). (c) The zinc-ribbon domain of Csl4 is required for exosome-mediated mRNA decay. The decay rate of PGK1pG-nonstop mRNA was measured in a wild-type strain (half-life = 2 min), a strain lacking the zinc-ribbon domain of Csl4 (half-life = 10 min) and a _ski7_Δ strain (half-life = 10 min). Shown is the average value from two independent experiments. The conclusion that the zinc-ribbon domain of Csl4 is required for exosome-mediated mRNA decay was confirmed using two other approaches (Supplementary Fig. 7).
The other two cap proteins, Rrp4 and Rrp40, each contain an N-terminal RPL27-like domain, a central S1 domain and a C-terminal KH domain. In contrast to Csl4, eight truncations of Rrp4 or Rrp40 each failed to complement _rrp4_Δ and _rrp40_Δ (Supplementary Fig. 5 online). Thus, the observation that the essential Csl4 does not contain any essential domains is specific for Csl4. Furthermore, the function of Rrp4 or Rrp40 could not be provided by chimeric proteins where one domain of Rrp4 was replaced by the paralogous Rrp40 domain (or vice versa), or by coexpressing two parts of Rrp4 (Supplementary Fig. 6 online). Overall, these results are consistent with Rrp4 and Rrp40 providing important bridging contacts for the PH-ring15. However, Csl4 does not seem to share this function.
A specific domain for exosome-mediated mRNA decay
Although the zinc-ribbon domain of Csl4 is not required for the essential exosome function(s), three assays each indicate that it is required for cytoplasmic exosome-mediated mRNA decay. First, PGK1-nonstop mRNA, which is normally rapidly degraded, is stabilized upon inactivation of the cytoplasmic exosome (for example, _ski7_Δ). The Csl4 truncation that deletes the zinc-ribbon domain results in a defect similar to _ski7_Δ (Fig. 4c). Second, the zinc ribbon is also required for the rapid degradation of the his3-nonstop mRNA (Supplementary Fig. 7 online). Third, a role of the exosome in general mRNA decay can be monitored through synthetic lethality with the dcp1-2 mutation, and this assay also indicates that the zinc ribbon of Csl4 is required for exosome-mediated mRNA decay (Supplementary Fig. 7). Therefore, the zinc-ribbon domain of Csl4 is not required for exosome structure or the essential exosome function(s), but it is required for cytoplasmic, exosome-mediated mRNA decay.
Discussion
A 5′ phosphate stimulates endoRNase in the exosome
We show for the first time that Rrp44 contains a previously overlooked endoRNase domain—the PIN domain. Two observations explain previous reports that Rrp44 with a mutation in the RNB domain has no nuclease activity in vitro21,24. First, the previously reported assays were carried out under conditions favorable for the activity of RNB domains (that is, in Tris buffer in the presence of Mg2+). Under similar conditions, we also failed to detect significant activity (Supplementary Fig. 1). Second, we observed robust endonuclease activity with truncated proteins, but much less activity with full-length protein or any truncations that did not remove the first cold shock domain (CSD1) present in many proteins of the RNase II family of enzymes (data not shown)26,37,38,39. This latter observation suggests that CSD1 and perhaps other domains of the exosome regulate the activity of the PIN domain. Nevertheless, the activity level of the truncated Rrp44 under conditions where PIN domains are generally active (that is, in HEPES buffer in the presence of Mn2+) was similar to the activity level of the full-length protein under conditions for the RNB domain (Supplementary Fig. 1). This suggests that, although the activity was not previously detected, it is robust and likely to be important in vivo under some circumstances or on some substrates that remain to be determined.
Our observation that Rrp44 needs either its endonuclease or exonuclease activity suggests that the endonuclease is active and important in vivo. Furthermore, such functional redundancy seems to be a general theme for a wide variety of RNases and is similar to that found for Rrp44 and Rrp6 in yeast21, Xrn1 and the exosome in yeast7,40, several combinations of Rex1, Rex2, Rex3 and Rrp6 in yeast5, and several exoRNase combinations in E. coli3,41.
In the process of testing 5′- or 3′-labeled substrates in in vitro degradation reactions, we noticed that substrates with a 5′ phosphate are more rapidly degraded than substrates with a 5′ hydroxyl or circular substrates. This is analogous to what has been described for bacterial RNase E, which prefers a 5′ monophosphate–containing substrate over a circular RNA or a linear RNA with a 5′ hydroxyl or 5′ triphosphate42. Despite this functional similarity, we have not detected any sequence similarity between Rrp44 and RNase E. The 5′ end–stimulated activity of Rrp44 might have several important consequences for the substrate specificity of the endonuclease activity. First, PIN domains are part of a large group of enzymes and ribozymes that use two-metal-ion catalysis28,29,30,32. All of these enzymes generate a 5′ cleavage product with a 3′ hydroxyl group and a 3′ cleavage product with a 5′ monophosphate (reviewed in ref. 43). This cleavage mechanism suggests that the endonuclease activity of Rrp44 might cleave most primary transcripts relatively inefficiently, but the 3′ cleavage product of an initial cleavage will have a 5′ phosphate and be a preferred substrate. Such preferred subsequent cleavage might ensure that RNA degradation is rapidly completed once it has been initiated. Second, many RNA species are processed both at the 5′ and 3′ end, and in most cases it is not clear how these events are coordinated. One possibility offered by our results is that 5′ end processing generates a 5′ monophosphate, which stimulates 3′ end processing by the Rrp44 endonuclease. Testing these hypotheses in detail will require the identification of all, or most, of the endogenous substrates on the endonuclease activity of Rrp44.
Functional specialization of an exosome domain
The exosome contains ten different essential subunits containing 21 domains. How this structural complexity correlates with the multiple functions of the exosome is not clear. To begin to address these questions, we generated many deletions of domains, both in Rrp44 and in the three cap proteins. The cap proteins have been suggested to be important for exosome structure, by simultaneously interacting with two different PH-ring subunits. The finding that the RPL27-like domain and S1 domain of Csl4 are not both essential is inconsistent with Csl4 providing important bridging interactions between subunits of the PH-ring, as deletion of the S1 and zinc-ribbon domains results in Csl4 interacting with only Mtr3 (Fig. 4a). Conversely, deletion of the RPL27-like domain results in Csl4 interacting with only Rrp43.
A high-throughput screen previously identified transposon insertions in the essential CSL4 gene44. Unexpectedly, these insertions are viable, a result that is explained by our observation that a severely truncated Csl4 protein is still functional. Similarly, T-DNA insertions into the Arabidopsis thaliana CSL4 gene are viable45. This observation was interpreted to mean that Csl4 is not an essential subunit of the A. thaliana exosome, but our results suggest the alternative explanation that the T-DNA mutants produce a truncated Csl4 that retains some function.
A corollary of the conclusion that Csl4 is not important for exosome structure is that it must be functionally important. One possible model is that Csl4 provides important contacts with either an essential substrate RNA or an essential cofactor. If such an RNA or protein molecule makes contacts with both the RPL27-like domain and the S1 or zinc-ribbon domains, it might still be able to interact if either binding site is deleted, but not if both are deleted. Notably, some surface-exposed conserved amino acid residues of the Csl4 zinc-ribbon domain that are not essential become essential if the RPL27-like domain is deleted (Supplementary Fig. 4). This is consistent with these residues forming one binding site and the RPL27-like domain containing a second binding site for an exosome cofactor. Csl4 is also thought to provide the binding sites for Ski7 (ref. 8); thus, Csl4 and perhaps the other cap proteins may provide important contacts for exosome cofactors, and may thus be important for specific exosome functions.
The exosome may have multiple ways to interact with RNA
It is not clear how the exosome interacts with RNA substrates. A crystal structure of the archaeal exosome in complex with RNA19 suggests that RNA might go through the center of the PH ring, as depicted in Figure 1a, above. Our conclusion that Csl4 provides important contacts for interaction with cytoplasmic cofactors seems most consistent with the suggestion that cytoplasmic mRNA follows this route. On the other hand, it has been proposed that RNA may gain access to Rrp44 without going through the PH ring25. The observation that the endonuclease activity is stimulated by a 5′ monophosphate indicates that Rrp44 can interact with the 5′ end of an exosome substrate. As the 3′ exoRNase active site must interact with the 3′ end, Rrp44 seems to be able to interact with both ends of substrate RNAs. This is unlikely to be compatible with threading the RNA through the PH ring. Thus, our observations seem to be more consistent with the idea that the exosome can interact with RNA substrates in two different ways (compare Fig. 1a, above, to Fig. 5). Moreover, we suggest that substrates that access Rrp44 directly might be identifiable by looking for substrates that are processed in vivo in a 5′ end–dependent manner.
Figure 5
A model of how RNA might access the 5′ end–stimulated endonuclease activity of Rrp44.
Convergence on combining RNases in mRNA decay machines
We show for the first time that the exosome contains both an endonuclease and exonuclease activity. Although this is unexpected for the exosome, it is not unique in nature. It has been suggested that the archaeal exosome also contains a PIN domain46, which could provide the archaeal exosome with an endonuclease activity. Similarly, the E. coli degradosome combines the RNase E endoRNase with the PNPase 3′ exoRNase47,48, and metazoan P-bodies combine the Argonaute endoRNase, the Xrn1 5′ exoRNase and the Ccr4, Caf1 and Pan2 3′ exoRNases49,50,51,52,53,54. Thus, the combination of endoRNases and exoRNases into one RNA-degrading machine is widespread in nature and has evolved multiple times independently, suggesting that such combination offers a fundamental advantage to the cell.
Note added in proof: After this manuscript was submitted, endonuclease activity of the Rrp44 PIN domain was also reported by others60.
Methods
Strains.
The strains, plasmid and oligonucleotides we used are described in detail in Supplementary Tables 1–3 online. The heterozygous diploids RRP44/_rrp44_Δ, CSL4/_csl4_Δ, RRP4/_rrp4_Δ and RRP40/_rrp40_Δ have been described and were obtained from Open Biosystems55. We transformed each of these strains with a URA3 plasmid that encoded the corresponding wild-type exosome subunit. We sporulated the transformants and obtained haploid progeny spores by the hydrophobic spore-isolation method essentially as described56. Isolated spores were germinated to generate the deletion strains complemented with the URA3 plasmid. The GAL::rrp44, GAL::csl4, GAL::rrp4 and GAL::rrp40 strains have been described previously and were obtained from P. Mitchell (University of Sheffield) and D. Tollervey (University of Edinburgh)10,11.
Plasmids.
All yeast plasmids used are low-copy plasmids that contain a yeast centromere and the endogenous promoter and 3′-flanking region to control expression of the exosome subunits. All were verified by sequencing.
To generate C-terminal truncations, we initially PCR amplified several hundred base pairs of the 3′-flanking region of the gene of interest and cloned it into pRS415 (ref. 57), which contains a LEU2 marker. We then PCR amplified the promoter and the desired part of the coding region and cloned it into the plasmid described above. N-terminal truncations were generated similarly, except that the promoter was PCR amplified and cloned first, and the truncated coding region and 3′-flanking region were added in the second step.
We generated GST-fusion plasmids by PCR amplifying the RRP44 coding region from the plasmids described above, digesting the PCR product with EcoRI and XhoI and ligating it into pGEX-4T-1 (GE Healthcare).
We created site-directed mutants using the QuikChange II kit (Stratagene). Each oligonucleotide also changes a restriction site. We screened putative mutants by restriction digestion and verified them by sequencing. To combine point mutations in the PIN domain of Rrp44 with the D551N mutant in the RNB domain, we digested the plasmids containing each single mutant with SacI and PshAI and ligated them together. PshAI cuts at a unique site within the CSD2 domain.
Overexpression and purification of recombinant Rrp44.
Full-length and truncated Rrp44 fused to GST were expressed in the Rosetta(DE3) E. coli strain. We grew cultures at 30 °C in 2 liters TB medium supplemented with 200 μg ml−1 ampicillin and 34 μg ml−1 chloramphenicol to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 1.2 and then induced expression by addition of 0.2 mM IPTG and incubation at 18 °C overnight. We harvested cells by centrifugation and froze them. Cells were thawed on ice, resuspended in 30 ml PBS buffer, pH 8, with 10 mM DTT and 1 mM PMSF, and lysed using the French press. We treated the crude extracts with 5 units Benzonase (Sigma) for 30 min at 0 °C, clarified the extract by a 30-min centrifugation at 10,000_g_, and loaded it onto a GSTrap™ FF 1-ml column (GE healthcare) equilibrated in binding buffer. We eluted proteins with a 0–10 mM glutathione gradient in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH8.5, 10 mM DTT. We pooled fractions containing the purified protein and loaded them onto a gel-filtration column (Superdex 75 10/300 GL or a Superose 12 10/300 GL, GE Healthcare, depending on the protein size) in 20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2 and 10 mM DTT buffer, pH 8. We concentrated the eluted protein by centrifugation at 15 °C with Vivaspin 500 Centrifugal Concentrators (Vivaspin). We determined protein concentrations by spectrophotometry using a Nanodrop and added 50% (v/v) glycerol to the final fractions before storage at −20 °C.
RNase assays.
RNase assays were based on those previously described. Briefly, each assay contained 100–500 nM protein, 200 nM 5′ or 3′ end–labeled U30 or A30 RNA or an internally labeled 5′ ETS RNA transcribed by T7 RNA polymerase, and 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 3 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT.
Growth assays.
We performed growth assays essentially as previously described9,58. Briefly, we grew strains in appropriate liquid selection media overnight at 30 °C (or 23 °C for temperature-sensitive mutants). We diluted these cultures in appropriate selection media to a starting OD600 of 0.2. We grew the cultures until they reached an OD of 0.8, serially diluted them in 96-well plates by a factor of five, and spotted them onto appropriate media. We generally incubated these plates for 2–3 d at 23 °C, 30 °C or 37 °C. To monitor the slow growth of Rrp44 truncations, we incubated the plates for up to 20 d.
Northern blotting.
Stability of PGK1-nonstop mRNA59, and 5.8S rRNA processing and 5′ ETS degradation59, were assayed as previously described.
Note: Supplementary information is available on the Nature Structural & Molecular Biology website.
References
- Moser, M.J., Holley, W.R., Chatterjee, A. & Mian, I.S. The proofreading domain of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I and other DNA and/or RNA exonuclease domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 5110–5118 (1997).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Mian, I.S. Comparative sequence analysis of ribonucleases HII, III, II PH and D. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3187–3195 (1997).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Deutscher, M.P. & Li, Z. Exoribonucleases and their multiple roles in RNA metabolism. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 66, 67–105 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Zuo, Y. & Deutscher, M.P. Exoribonuclease superfamilies: structural analysis and phylogenetic distribution. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 1017–1026 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - van Hoof, A., Lennertz, P. & Parker, R. Three conserved members of the RNase D family have unique and overlapping functions in the processing of 5S, 5.8S, U4, U5, RNase MRP and RNase P RNAs in yeast. EMBO J. 19, 1357–1365 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Muhlrad, D., Decker, C.J. & Parker, R. Turnover mechanisms of the stable yeast PGK1 mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2145–2156 (1995).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Jacobs Anderson, J.S. & Parker, R. The 3′ to 5′ degradation of yeast mRNAs is a general mechanism for mRNA turnover that requires the SKI2 DEVH box protein and 3′ to 5′ exonucleases of the exosome complex. EMBO J. 17, 1497–1506 (1998).
Article Google Scholar - van Hoof, A., Frischmeyer, P.A., Dietz, H.C. & Parker, R. Exosome-mediated recognition and degradation of mRNAs lacking a termination codon. Science 295, 2262–2264 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Meaux, S. & Van Hoof, A. Yeast transcripts cleaved by an internal ribozyme provide new insight into the role of the cap and poly(A) tail in translation and mRNA decay. RNA 12, 1323–1337 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Mitchell, P., Petfalski, E., Shevchenko, A., Mann, M. & Tollervey, D. The exosome: a conserved eukaryotic RNA processing complex containing multiple 3′ → 5′ exoribonucleases. Cell 91, 457–466 (1997).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Allmang, C. et al. The yeast exosome and human PM-Scl are related complexes of 3′ → 5′ exonucleases. Genes Dev. 13, 2148–2158 (1999).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Allmang, C. et al. Functions of the exosome in rRNA, snoRNA and snRNA synthesis. EMBO J. 18, 5399–5410 (1999).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - van Hoof, A., Lennertz, P. & Parker, R. Yeast exosome mutants accumulate 3′-extended polyadenylated forms of U4 small nuclear RNA and small nucleolar RNAs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 441–452 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - de la Cruz, J., Kressler, D., Tollervey, D. & Linder, P. Dob1p (Mtr4p) is a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase required for the 3′ end formation of 5.8S rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 17, 1128–1140 (1998).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Liu, Q., Greimann, J.C. & Lima, C.D. Reconstitution, activities, and structure of the eukaryotic RNA exosome. Cell 127, 1223–1237 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Lorentzen, E. et al. The archaeal exosome core is a hexameric ring structure with three catalytic subunits. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 575–581 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Symmons, M.F., Jones, G.H. & Luisi, B.F. A duplicated fold is the structural basis for polynucleotide phosphorylase catalytic activity, processivity, and regulation. Structure 8, 1215–1226 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Navarro, M.V., Oliveira, C.C., Zanchin, N.I. & Guimaraes, B.G. Insights into the mechanism of progressive RNA degradation by the archaeal exosome. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 14120–14131 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Lorentzen, E. & Conti, E. Structural basis of 3′ end RNA recognition and exoribonucleolytic cleavage by an exosome RNase PH core. Mol. Cell 20, 473–481 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Buttner, K., Wenig, K. & Hopfner, K.P. Structural framework for the mechanism of archaeal exosomes in RNA processing. Mol. Cell 20, 461–471 (2005).
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Dziembowski, A., Lorentzen, E., Conti, E. & Seraphin, B. A single subunit, Dis3, is essentially responsible for yeast exosome core activity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 15–22 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chekanova, J.A., Dutko, J.A., Mian, I.S. & Belostotsky, D.A. Arabidopsis thaliana exosome subunit AtRrp4p is a hydrolytic 3′ → 5′ exonuclease containing S1 and KH RNA-binding domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 695–700 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Lorentzen, E., Basquin, J., Tomecki, R., Dziembowski, A. & Conti, E. Structure of the active subunit of the yeast exosome core, Rrp44: diverse modes of substrate recruitment in the RNase II nuclease family. Mol. Cell 29, 717–728 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Schneider, C., Anderson, J.T. & Tollervey, D. The exosome subunit Rrp44 plays a direct role in RNA substrate recognition. Mol. Cell 27, 324–331 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Wang, H.W. et al. Architecture of the yeast Rrp44 exosome complex suggests routes of RNA recruitment for 3′ end processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 16844–16849 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Frazão, C. et al. Unravelling the dynamics of RNA degradation by ribonuclease II and its RNA-bound complex. Nature 443, 110–114 (2006).
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Barbas, A. et al. New insights into the mechanism of RNA degradation by ribonuclease II: identification of the residue responsible for setting the RNase II end product. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13070–13076 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Arcus, V.L., Backbro, K., Roos, A., Daniel, E.L. & Baker, E.N. Distant structural homology leads to the functional characterization of an archaeal PIN domain as an exonuclease. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 16471–16478 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Levin, I. et al. Crystal structure of a PIN (PilT N-terminus) domain (AF0591) from Archaeoglobus fulgidus at 1.90 resolution. Proteins 56, 404–408 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Glavan, F., Behm-Ansmant, I., Izaurralde, E. & Conti, E. Structures of the PIN domains of SMG6 and SMG5 reveal a nuclease within the mRNA surveillance complex. EMBO J. 25, 5117–5125 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Daines, D.A., Wu, M.H. & Yuan, S.Y. VapC-1 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae is a ribonuclease. J. Bacteriol. 189, 5041–5048 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Bunker, R.D., McKenzie, J.L., Baker, E.N. & Arcus, V.L. Crystal structure of PAE0151 from Pyrobaculum aerophilum, a PIN-domain (VapC) protein from a toxin-antitoxin operon. Proteins 72, 510–518 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Eberle, A.B., Lykke-Andersen, S., Muhlemann, O. & Jensen, T.H. SMG6 promoted endonucleoytic cleavage of nonsense mRNA in human cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. advance online publication, doi:10.1038/nsmb.1530 (07 December 2008).
- Fatica, A., Tollervey, D. & Dlakic, M. PIN domain of Nob1p is required for D-site cleavage in 20S pre-rRNA. RNA 10, 1698–1701 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Bleichert, F., Granneman, S., Osheim, Y.N., Beyer, A.L. & Baserga, S.J. The PINc domain protein Utp24, a putative nuclease, is required for the early cleavage steps in 18S rRNA maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 9464–9469 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Amblar, M. & Arraiano, C.M. A single mutation in Escherichia coli ribonuclease II inactivates the enzyme without affecting RNA binding. FEBS J. 272, 363–374 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Amblar, M., Barbas, A., Fialho, A.M. & Arraiano, C.M. Characterization of the functional domains of Escherichia coli RNase II. J. Mol. Biol. 360, 921–933 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Barbas, A. et al. New insights into the mechanism of RNA degradation by ribonuclease II: identification of the residue responsible for setting the RNase II end product. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13070–13076 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Cairrao, F., Arraiano, C. & Newbury, S. Drosophila gene tazman, an orthologue of the yeast exosome component Rrp44p/Dis3, is differentially expressed during development. Dev. Dyn. 232, 733–737 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Johnson, A.W. & Kolodner, R.D. Synthetic lethality of sep1 (xrn1) ski2 and sep1 (xrn1) ski3 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is independent of killer virus and suggests a general role for these genes in translation control. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2719–2727 (1995).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Andrade, J.M., Pobre, V., Silva, I.J., Domingues, S. & Arraiano, C.M. The role of 3′ to 5′ exonucleases in RNA degradation. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. (in the press).
- Mackie, G.A. Ribonuclease E is a 5′-end-dependent endonuclease. Nature 395, 720–723 (1998).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Yang, W. An equivalent metal ion in one- and two-metal-ion catalysis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 1228–1231 (2008).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Ross-Macdonald, P. et al. Large-scale analysis of the yeast genome by transposon tagging and gene disruption. Nature 402, 413–418 (1999).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chekanova, J.A. et al. Genome-wide high-resolution mapping of exosome substrates reveals hidden features in the Arabidopsis transcriptome. Cell 131, 1340–1353 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Koonin, E.V., Wolf, Y.I. & Aravind, L. Prediction of the archaeal exosome and its connections with the proteasome and the translation and transcription machineries by a comparative-genomic approach. Genome Res. 11, 240–252 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Carpousis, A.J., Van Houwe, G., Ehretsmann, C. & Krisch, H.M. Copurification of E. coli RNAase E and PNPase: evidence for a specific association between two enzymes important in RNA processing and degradation. Cell 76, 889–900 (1994).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Py, B., Causton, H., Mudd, E.A. & Higgins, C.F. A protein complex mediating mRNA degradation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 14, 717–729 (1994).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Liu, J., Valencia-Sanchez, M.A., Hannon, G.J. & Parker, R. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 719–723 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Ingelfinger, D., Arndt-Jovin, D.J., Luhrmann, R. & Achsel, T. The human LSm1–7 proteins colocalize with the mRNA-degrading enzymes Dcp1/2 and Xrnl in distinct cytoplasmic foci. RNA 8, 1489–1501 (2002).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Bashkirov, V.I., Scherthan, H., Solinger, J.A., Buerstedde, J.M. & Heyer, W.D. A mouse cytoplasmic exoribonuclease (mXRN1p) with preference for G4 tetraplex substrates. J. Cell Biol. 136, 761–773 (1997).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Cougot, N., Babajko, S. & Seraphin, B. Cytoplasmic foci are sites of mRNA decay in human cells. J. Cell Biol. 165, 31–40 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Zheng, D. et al. Deadenylation is prerequisite for P-body formation and mRNA decay in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 182, 89–101 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Andrei, M.A. et al. A role for eIF4E and eIF4E-transporter in targeting mRNPs to mammalian processing bodies. RNA 11, 717–727 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Giaever, G. et al. Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 418, 387–391 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Rockmill, B., Lambie, E.J. & Roeder, G.S. Spore enrichment. Methods Enzymol. 194, 146–149 (1991).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Sikorski, R.S. & Hieter, P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 122, 19–27 (1989).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Wilson, M.A., Meaux, S. & van Hoof, A. A genomic screen in yeast reveals novel aspects of nonstop mRNA metabolism. Genetics 177, 773–784 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - van Hoof, A., Staples, R.R., Baker, R.E. & Parker, R. Function of the ski4p (Csl4p) and Ski7p proteins in 3′-to-5′ degradation of mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 8230–8243 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Lebreton, A., Tomecki, R., Dziembowski, A. & Séraphin, B. Endonucleolytic RNA cleavage by a eukaryotic exosome. Nature advance online publication, doi:10.1038/nature07480 (7 December 2008).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to T. Link and R. Brennan for help with calculating the buried surfaces between the different domains of the cap proteins and the PH ring, and A. Klauer for technical assistance. GAL::rrp44, GAL::csl4, GAL::rrp4 and GAL::rrp40 strains were kindly provided by P. Mitchell (University of Sheffield) and D. Tollervey (University of Edinburgh). R. Parker, M. Wilkinson, M. Steiger and members of the van Hoof and Arraiano laboratories gave insightful comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by the Pew Scholarship Program in the Biomedical Sciences and by the National Institutes of Health (GM069900) to A.v.H. E.G.D and M.S.-R. were supported by The University of Texas at Houston Medical School-Summer Research Program. The work at the Instituto de Tecnologia Química e Biológica was supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal. A.B. was a recipient of a post-doctoral fellowship from FCT, Portugal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, University of Texas Health Science Center-Houston, 6431 Fannin Street, MSB 1.212, Houston, 77030, Texas, USA
Daneen Schaeffer, Borislava Tsanova, Eeshita Ghosh Dastidar, Maya Sanchez-Rotunno & Ambro van Hoof - Instituto de Tecnologia Química e Biológica, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Apartado 127, Oeiras, 2781-901, Portugal
Ana Barbas, Filipa Pereira Reis & Cecília Maria Arraiano
Authors
- Daneen Schaeffer
- Borislava Tsanova
- Ana Barbas
- Filipa Pereira Reis
- Eeshita Ghosh Dastidar
- Maya Sanchez-Rotunno
- Cecília Maria Arraiano
- Ambro van Hoof
Corresponding author
Correspondence toAmbro van Hoof.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaeffer, D., Tsanova, B., Barbas, A. et al. The exosome contains domains with specific endoribonuclease, exoribonuclease and cytoplasmic mRNA decay activities.Nat Struct Mol Biol 16, 56–62 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1528
- Received: 06 November 2008
- Accepted: 13 November 2008
- Published: 07 December 2008
- Issue Date: January 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1528
This article is cited by
You have full access to this article via your institution.