Unbounded Variable-Size Signals - MATLAB & Simulink (original) (raw)
In Simulink®, variable-size signals are signals whose size (the number of elements in a dimension), in addition to its values can change during model simulation. For example, a variable-size signal with dimensions [2 5] allows the first dimension to vary in the range of [0 2] and the second dimension to vary in the range of[0 5].
Unbounded variable-size signals or dynamic arrays extend the functionality of variable-size signals by modeling data whose sizes are unknown during model compilation. You can configure an unbounded variable-size signal by specifying the size of a variable-size signal as Inf. For example, an unbounded variable-size signal with dimension [2 Inf] allows the first dimension to vary in the range of[0 2] and the second dimension in the range of [0 intmax("int32")]. intmax("int32") indicates the maximum allowable size limit. For more information, see Maximum Size Limits of Simulink Models.
Unbounded variable-size signals use dynamic memory allocation and deallocation to react to varying signal sizes during model simulation. This functionality allows efficient storage and management of signal data.
Unbounded variable-size signals can be beneficial in these scenarios:
- Data storage — Unbounded variable-size signals gives you the flexibility to model signals without specifying a potentially conservative finite signal size (upper bound), resulting in more efficient use of available memory.
- Code generation — When you interface code generated from Simulink models with external libraries or APIs that operate on dynamic arrays, using unbounded variable-size signals allow Simulink code components to easily exchange data with other external software components. For more information, Variable-Size Signals in Generated Code (Simulink Coder).
This table describes the differences between bounded and unbounded variable-size signals.
| Attribute | Bounded Variable-Size Signals | Unbounded Variable-Size Signals |
|---|---|---|
| Signal size | Specify a finite signal size for model compilation. | Specify signal size as Inf for model compilation. |
| Memory allocation | Memory is allocated statically at run time based on the signal size specified for model compilation. | Memory is allocated dynamically based on the signal size during model simulation. |
| Code generation | Suitable for deployment to memory constrained embedded targets. | Suitable for deployment to desktop quality targets. |
Note
To ensure optimal model configuration and avoid workflow errors, it is recommended to avoid using both unbounded and bounded variable-size signals in the same model.
Using Unbounded Variable-Size Signals
Follow these steps to use unbounded variable-size signals in a model.
Determine Whether Model Meets Requirements
Determine whether your model meets the requirements to use unbounded variable-size signals.
- For each model component and for component interfaces, identify the signals whose sizes are unknown at model compilation.
- Check if the source and sink blocks for the signals support unbounded variable-size signals:
- If the blocks are not supported, you must define finite values for all the dimensions of such signals. In this case, the next steps and sections do not apply to your model.
- If the blocks are supported, proceed to the next step. For more information about the blocks supported, see Supported Blocks.
- If the blocks are supported but the model features are not supported, you must change to supported model features. For more information, see Supported Features.
Configure Model Components
Configure the model based on whether signals are associated with blocks or contained in signal or bus objects.
These are four typical configuration scenarios:
- Unbounded variable-size signals associated with the Inport block
- Unbounded variable-size signals associated with the input or output port of theMATLAB Function block
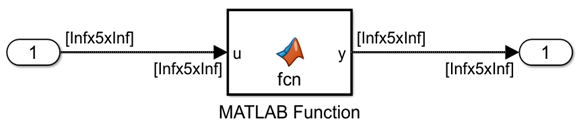
- Unbounded variable-size
Simulink.BusElementobjects contained in Simulink.Bus object
- Unbounded variable-size Simulink.Signal object
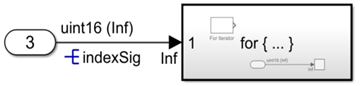
For more information, see Unbounded Variable-Size Signal Basic Operations.
Compile Model and Verify Signal Dimensions
Verify if the model is configured to handle unbounded variable-size signals.
- Update the block diagram (Ctrl+D).
- In the Simulink Editor, on the Debug tab, selectInformation Overlays and click Signal Dimensions.
- Each signal is labeled with its dimensions, so you can check that the signals are properly configured to carry unbounded size data.
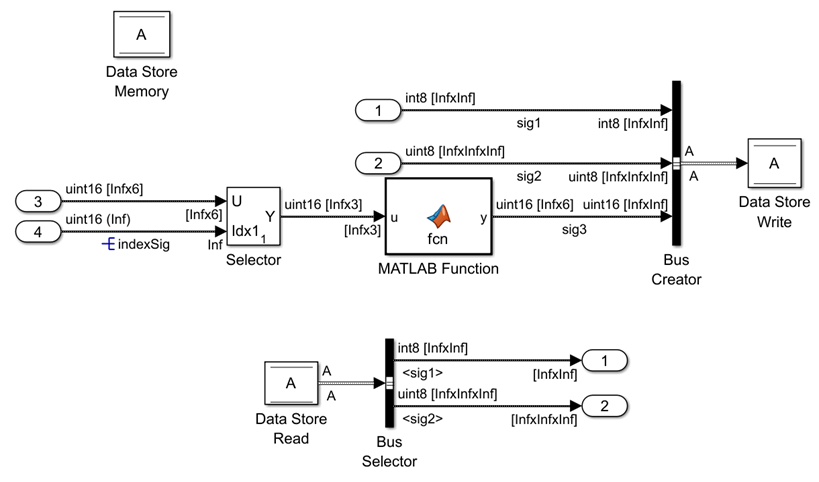
Prepare Model for Simulation
To prepare the model for simulation, in the Configuration Parameters dialog box:
- In the Solver pane, in the Solver Selection section, check that Solver is set to the default
autooption. Otherwise, selectauto(Automatic Solver Selection)ordiscrete(no continuous states). Unbounded variable-size signals only support discrete solvers. - In the pane, check that the data logging Format is set to
Dataset(default).
Set Up Data Logging
You can log unbounded variable-size signals using any of the mechanism described inView the Signal Logging Configuration. Logging non-virtual buses that contain unbounded variable-size signals is not supported.
Unbounded Variable-Size Signals in C++ Code Generation
Configure the model for code generation. In the Code Generation pane:
- Set the target language to
C++. - In the Interface section, select Support: variable-size signals.
For more information about code generation, see Variable-Size Signals in Generated Code (Simulink Coder).
Unbounded Variable-Size Arrays in MATLAB Function Block
You must use MATLAB Function blocks to implement math operations for unbounded variable-size signals, because nonvirtual mathematical operation blocks are not supported.
When using a MATLAB Function block, in the pane:
- In Advanced parameters section, check that Dynamic memory allocation in MATLAB functions is selected. This option is selected by default. For more information, see Declare Variable-Size MATLAB Function Block Variables.
- Set Language as
C++.
When using unbounded variable-size signals, MATLAB Function blocks use dynamic memory allocation. For more information, see Use Dynamic Memory Allocation for Variable-Size Arrays in a MATLAB Function Block.
For an example that has a MATLAB Function block which uses unbounded variable-size arrays, see Unbounded Variable-Size Signal Basic Operations.
Supported Blocks and Features for Simulation
This section lists blocks and features that you can use with unbounded variable-size signals. Any block or feature not listed in this section is not supported.
Supported Blocks
These Simulink blocks support unbounded variable-size signals. The list below shows the blocks based on the Simulink library they belong to. To access the Simulink Library Browser, in the Simulink Toolstrip, on the Simulation tab, clickLibrary Browser.
- Simulink / Port & Subsystems
- Simulink / Signal Attributes
- Simulink / User-Defined Functions
- Simulink Function
- MATLAB Function
- S-Function
- Function Caller
- Starting in R2025a, MATLAB System block is supported.
- Simulink / Signal Routing
- Simulink / Sources
- Simulink / Sinks
- Simulink / Math Operations
Supported Features
- Normal simulation mode for top-level model in a model hierarchy
- Both normal and accelerator simulation modes for referenced models
- All data types except string