Pentane - Thermophysical Properties (original) (raw)
Pentane, C5 H 12 , is a clear colorless liquid with a petroleum-like odor. It belongs to the organic class alkanes, and is naturally present in crude oils and condensates. It is a component of some fuels and is employed as a specialty solvent in the laboratory.
The boling point 36°C/97°F, and the vapors are heavier than air. Both the liquid an the vapor are flammable.
The phase diagram of pentane is shown below the table.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of pentane :
Values are given for liquid at 25 oC /77 oF / 298 K and 1 bara, if not other phase, temperature or pressure given.
For full table with Imperial Units - rotate the screen!
Pentane - Thermophysical Properties
| Property | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoignition temperature | 533 | K | 260 | °C | 500 | °F | ||
| Boiling Point | 309.2 | K | 36.06 | °C | 96.9 | °F | ||
| Critical density | 3.22 | mol/dm3 | 232 | kg/m3 | 0.450 | slug/ft3 | 14.5 | lb/ft3 |
| Critical pressure | 3.36 | MPa=MN/m2 | 33.6 | bar | 33.2 | atm | 487 | psi=lbf/in2 |
| Critical temperature | 469.8 | K | 196.7 | °C | 386.0 | °F | ||
| Critical volume | 311 | cm3 /mol | 0.00431 | m3 /kg | 2.22 | ft3 /slug | 0.0690 | ft3 /lb |
| Density | 8606 | mol/m3 | 620.9 | kg/m3 | 1.205 | slug/ft3 | 38.76 | lb/ft3 |
| Flammable, gas and liquid | yes | |||||||
| Flash point | 224 | K | -49 | °C | -56 | °F | ||
| Gas constant , individual, R | 115.2 | J/kg K | 0.03201 | Wh/(kg K) | 689.1 | [ft lbf /slug °R] | 21.42 | [ft lbf /lb °R] |
| Gibbs free energy of formation (gas) | -8 | kJ/mol | -111 | kJ/kg | -48 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of combustion (gas) | -3535 | kJ/mol | -48996 | kJ/kg | -21.1 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of combustion (liquid) | -3509 | kJ/mol | -48636 | kJ/kg | -20.9 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of formation (gas) | -147.0 | kJ/mol | -2037 | kJ/kg | -876 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of formation (liquid) | -173 | kJ/mol | -2398 | kJ/kg | -1031 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of fusion at -202 °F/-130°C | 8.4 | kJ/mol | 116 | kJ/kg | 50.05 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of sublimation, at -202°F/-130°C | 42 | kJ/mol | 582 | kJ/kg | 250 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of evaporation | 26.4 | kJ/mol | 366 | kJ/kg | 157 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat capacity , Cp (gas) | 120.0 | J/mol K | 1.66 | kJ/kg K | 0.397 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | ||
| Specific heat, Cp (liquid) | 168.0 | J/mol K | 2.33 | kJ/kg K | 0.556 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | ||
| Specific heat, Cv (liquid) | 125.0 | J/mol K | 1.73 | kJ/kg K | 0.414 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | ||
| Ionization potential | 10.34 | eV | ||||||
| log KOW (Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient) | 3.39 | |||||||
| Melting point | 143.48 | K | -129.7 | °C | -201.4 | °F | ||
| Molecular Weight | 72.149 | g/mol | 0.15906 | lb/mol | ||||
| Solubility in water, at 25°C | 0.038 | mg/ml | ||||||
| Sound velocity | 1012 | m/s | 3319 | ft/s | 2267 | mi/h | ||
| Specific Gravity (gas) (relativ to air) | 2.48 | |||||||
| Specific Gravity (liquid) (relativ to water) | 0.63 | |||||||
| Specific Heat Ratio (gas) - CP /CV | 1.09 | |||||||
| Specific Heat Ratio (liquid) - CP /CV | 1.34 | |||||||
| Specific Volume | 0.0001162 | m3 /mol | 0.0016106 | m3 /kg | 0.8300514 | ft3 /slug | 0.0257988 | ft3 /lb |
| Standard molar entropy , S° (gas) | 348 | J/mol K | 4.82 | kJ/kg K | 1.15 | Btu/lb °F | ||
| Standard molar entropy, S° (liquid) | 263 | J/mol K | 3.65 | kJ/kg K | 0.87 | Btu/lb °F | ||
| Surface tension | 16.0 | dynes/cm | 0.016 | N/m | ||||
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.111 | W/m°C | 0.064135 | Btu/hr ft °F | ||||
| Triple point pressure | 7.63*10-8 | MPa=MN/m2 | 7.63*10 -7 | bar | 7.53*10 -7 | atm | 1.11*10 -5 | psi=lbf/in2 |
| Triple point temperature | 143.5 | K | -129.7 | °C | -201.46 | °F | ||
| Vapor (saturation) pressure | 0.0685 | MPa=MN/m2 | 514.0 | mm Hg | 0.6762 | atm | 9.94 | psi=lbf/in2 |
| Viscosity , dynamic (absolute) | 0.2224 | cP | 149.4 | [lbm /ft s*10-6 ] | 4.64 | [lbf s/ft2*10-6 ] | ||
| Viscosity, kinematic | 0.358 | cSt | 3.9 | [ft2/s*10-6 ] |
Density of pentane with varying temperature and pressure
See also more about atmospheric pressure , and STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure & NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure ,
as well as Thermophysical properties of: Acetone , Acetylene , Air , Ammonia , Argon , Benzene , Butane , Carbon dioxide , Carbon monoxide , Ethane , Ethanol , Ethylene , Helium , Hydrogen , Hydrogen sulfide , Methane , Methanol , Nitrogen , Oxygen , Propane , Toluene , Water and Heavy water, D2O .
Pentane is a liquid at standard conditions. However, if heated above 36°C/97°F it becomes a gas, and when cooled it becomes a solid. The phase diagram for pentane shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the pentane boiling point with changes in pressure. It also shows the saturation pressure with changes in temperature.
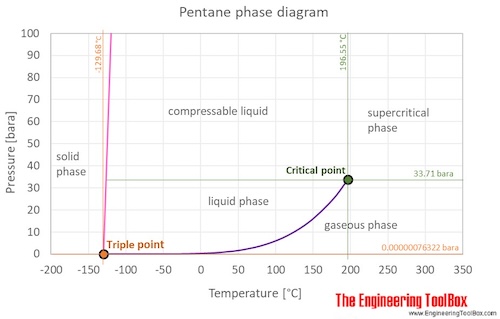
At the critical point there is no change of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added.
The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Acetylene.
Thermal properties of air at different temperatures - density, viscosity, critical temperature and pressure, triple point, enthalpi and entropi, thermal conductivity and diffusivity and more.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ammonia. Phase diagram included.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Argon.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of benzene, also called benzol. Phase diagram included.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of n-Butane.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of carbon dioxide. Phase diagram included.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Carbon Monoxide - CO.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ethane - C2H6.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethanol (also called alcohol or ethyl alcohol). Phase diagram included.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethylene, also called ethene, acetene and olefiant gas. Phase diagram included.
Thermodynamic properties of heavy water (D2O) like density, melting temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of fusion, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Helium - He.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Hydrogen - H2.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of hydrogen sulfide, H2S, also called hydrosulfuric acid, sewer gas and stink damp. Phase diagram included.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Methane - CH4. Phase diagram included.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of methanol, CH3OH (also called carbinol, wood alcohol, hydroxy methyl and methyl alcohol). Phase diagram included.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Nitrogen - N2.
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Oxygen - O2.
Online calculator, figures and table showing density and specific weight of pentane, C5H12, at temperatures ranging from -130 to 325 °C (-200 to 620 °F) at atmospheric and higher pressure - Imperial and SI Units.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of propane gas - C3H8.
Thermal properties of water at different temperatures like density, freezing temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of melting, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more.